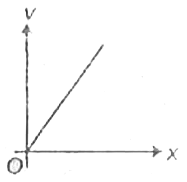
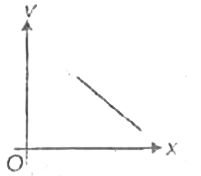
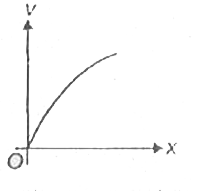
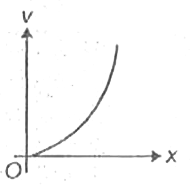
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - B)|33 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - C)|37 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise EXERCISE|30 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignement section -J (Aakash Challengers Questions)|4 VideosMOTION IN STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - J)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE-ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - A)
- A boy throws balls into air at regular interval of 2 second. The next ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball projected from ground vertically upward is at same height at ti...
Text Solution
|
- For a body moving with uniform acceleration along straight line, the v...
Text Solution
|
- The position - time graph for a particle moving along a straight line ...
Text Solution
|
- The position - time graph for a body moving along a straight line betw...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following graph for a body moving along a straight line i...
Text Solution
|
- A body is projected vertically upward from ground. If we neglect the e...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following position-time graphs correctly represents two m...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement - time graph for two particles A and B is as follows....
Text Solution
|
- For the acceleration - time (a - t) graph shown in figure, the change ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the graph of x - coordinate of a particle moving along x ...
Text Solution
|
- Position - time graph for a particle is shown in figure. Starting from...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity versus time graph of a body moving in a straight line is ...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration - time graph for a particle is given in figure. If it sta...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the position of a particle moving on the x - axis as a fu...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along x - axis in such a way that its x - co - ordina...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls are projected upward simultaneously with speeds 40 m/s and 6...
Text Solution
|
- The position (x) of a particle moving along x - axis veries with time ...
Text Solution
|
- The position (x) - time (t) graph for a particle moving along a straig...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a height h above ground. Neglect the air resist...
Text Solution
|