Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise MATCHING THE COLUMNS|4 VideosHYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|2 VideosHYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosHYDROCARBONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise Long Answer Type Questions|4 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise Long Answer type question|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-HYDROGEN-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- How can production of hydrogen from water gas be increased by usin...
Text Solution
|
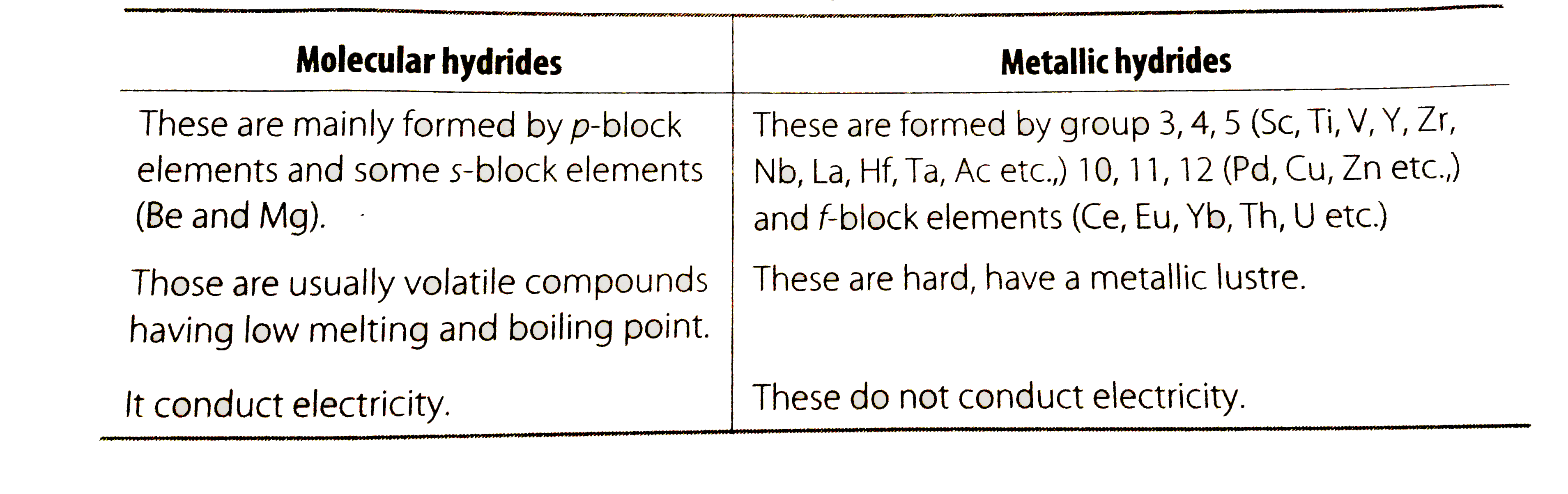
- What are metallic or interstitial hydrides? How do they differ from mo...
Text Solution
|
- Name the classes of hydrides to which H(2)O, B(2)H(6) and NaH belo...
Text Solution
|
- If same mass of liquid water and a piece of ice is taken, then why...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following equations (i) PbS(s) +H(2)O(2) (aq) to ...
Text Solution
|
- Given reasons (i) Lakes freeze form top towards bottom. (ii) Ice ...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by the term 'auto-protolysis' of water? What is...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss briefly de- mineralisation of water by ion exchange resin.
Text Solution
|
- Molecular hydrides are classified as electron deficient, electron pre...
Text Solution
|
- How is heavy water prepared? Compare its physical properties with ...
Text Solution
|
- Write one chemical reactions for the preparation of D(2)O(2).
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the strenght of 5 volumes H(2)O(2) solution.
Text Solution
|
- (i) Draw the gas phase and solid phase structure of H(2)O(2). (ii...
Text Solution
|
- Melting point, enthaply of vaporisation and visvocsity data of H(2...
Text Solution
|
- Dihydrogen reacts with dioxygen (O(2)) to from water .Write the na...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why HCl is a gas and HF is a liquid ?
Text Solution
|
- When the first element of the periodic table is treated with diox...
Text Solution
|
- Rohan heard that instructions were given to the laboratory attend...
Text Solution
|
- Given reason why hydrogen resembles alkali metals ?
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen generally form covalent compounds. Give reason
Text Solution
|