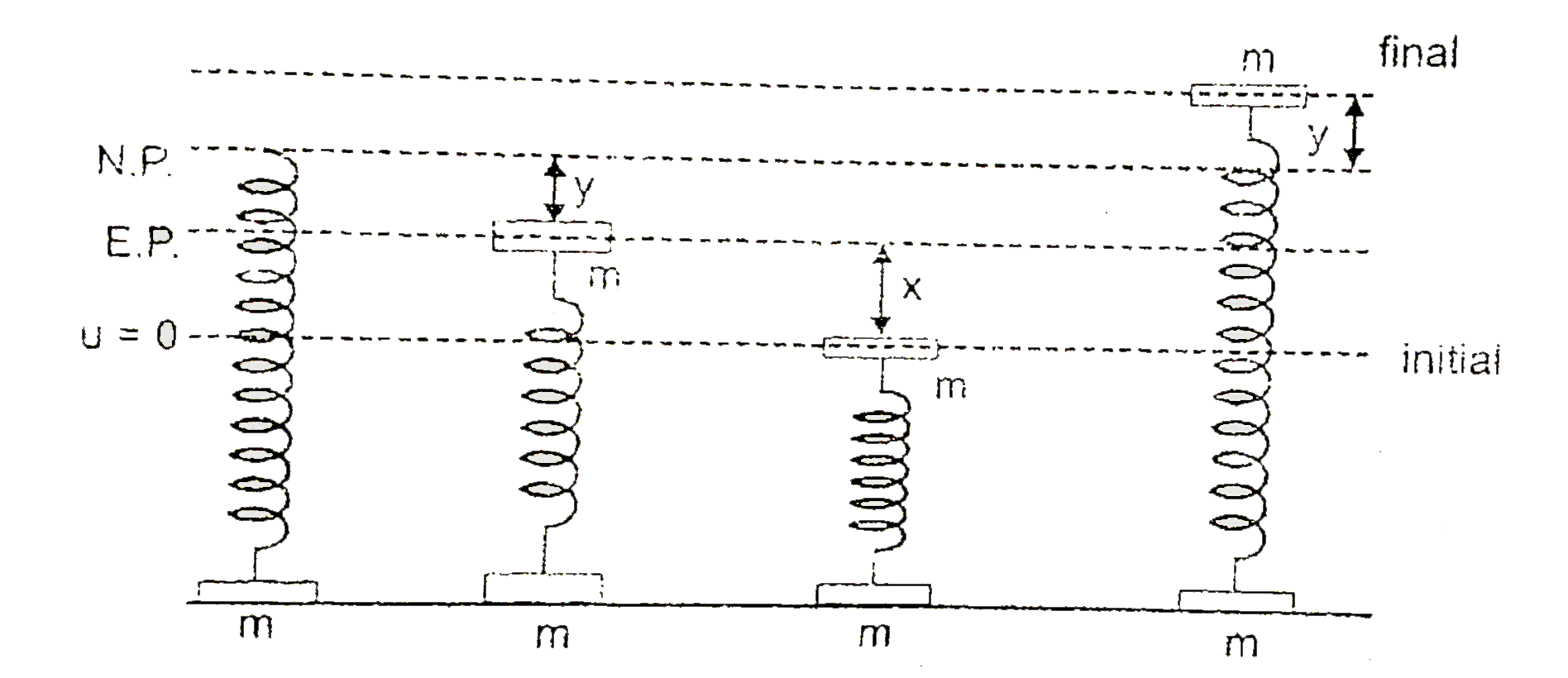
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 2, PART - II|1 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 2, PART - III|12 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 1, PART - II|37 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 3|88 VideosTEST PAPERS
RESONANCE|Exercise FST-3|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -Exercise- 2, PART - I
- The potential energy of a peticle of mass 'm' situated in a unidimensi...
Text Solution
|
- A solid ball of mass m is made to fail from a height H on a pan suspen...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates of some mass are attached rigidly to the two ends of a spri...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs, each of spring constant k, are attached to a block of mas...
Text Solution
|
- The right block in figure moces at a speed V towards the left block pl...
Text Solution
|
- The bob of a simple pendulum of length L is released at time t = 0 fro...
Text Solution
|
- The period of small oscillations of a simple pendulum of length l if i...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum , a physical pendulum, a torsional pendulum and a sp...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass M and length L is hinged at its one end and carries a pa...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along the X-axis according to the equation x = 10 sin...
Text Solution
|
- The amplitide of a particle due to superposition of following S.H.Ms. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles P and Q describe S.H.M. of same amplitude a, same freque...
Text Solution
|
- A street car moves rectilinearly from station A (here car stops) to th...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is oscillating in a stright line about a centre of force O,...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming all the surfaces to be smoth, if the time period of motion of...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is attached with three springs A,B and C of equal...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown mass 2m is at rest and in equilibrium. A particle ...
Text Solution
|
- For given spring mass system, if the time period of small oscillations...
Text Solution
|
- For the arrangement shown in figure, the spring is initially compresse...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block is eecuting simpe hrmonic motion of ampliltude 0.1 m m on ...
Text Solution
|