Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-1
- An object of height 1cm is set at angles to the optical axis of a dou...
Text Solution
|
- A lens placed between a candle and a fixed screen forms a real tr...
Text Solution
|
- A pin of length 1cm lies along the principle axis of a converging len...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the sun is 0.75xx10^(8)m and its distance from the eart...
Text Solution
|
- A 2.5 dipote lens forms a virtual image which is 4 times the obje...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially 5 cm toward...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens and a convex mirror are placed at a separation fo 15cm...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed on the principle axis of a converging len...
Text Solution
|
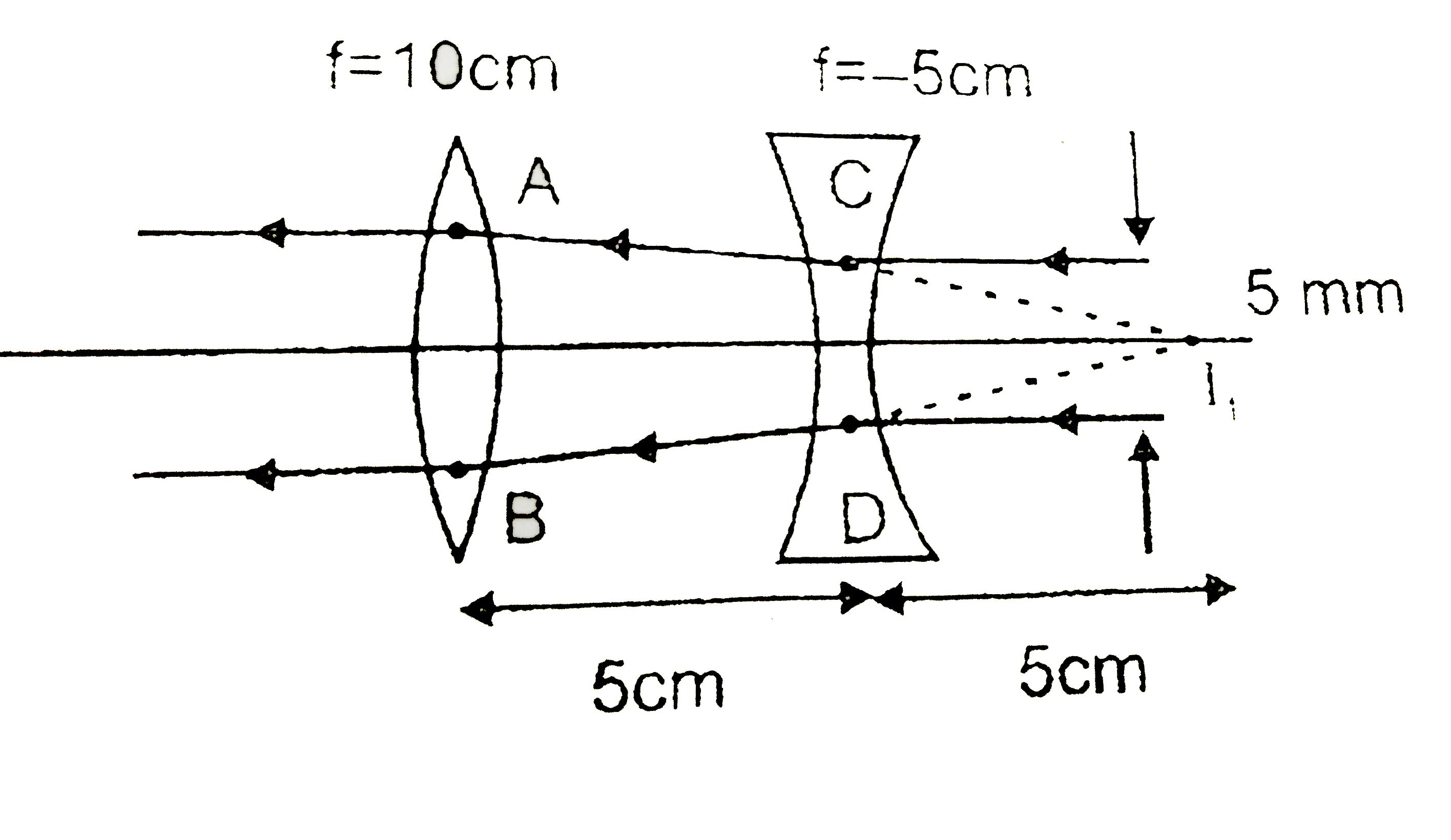
- A converging lens of focal length 10cm and a diverging lens of focal l...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical thin converging lenses brought in contact so that thei...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens. Th...
Text Solution
|
- The convex surface of a thin concave-convex lens of glass of refractiv...
Text Solution
|
- A certiain material has refractive indices 1.53, 1.60 and 1.68 for re...
Text Solution
|
- A flint glass prism and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such...
Text Solution
|
- Three thin prisms are combind as shwon in figure. The refractive indi...
Text Solution
|
- The focal lenghts of a convex lens for red, yellow and violet rays ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin prism of angle 5.0^(@), omega = 0.07 and mu(y) = 1.30 is comine...
Text Solution
|
- A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 144 cm and an ...
Text Solution
|
- An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30 X is desired using a...
Text Solution
|
- A compound microscope has an objective of focal length 2.0 cm and an e...
Text Solution
|