Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ELECTRODYNAMICS-Exercise-1 PART-1
- An electron gun G emits electons of energy 2 keV travelling in the pos...
Text Solution
|
- An electron beam passes through a magnetic field of 2xx10^(-3) Wb//m^(...
Text Solution
|
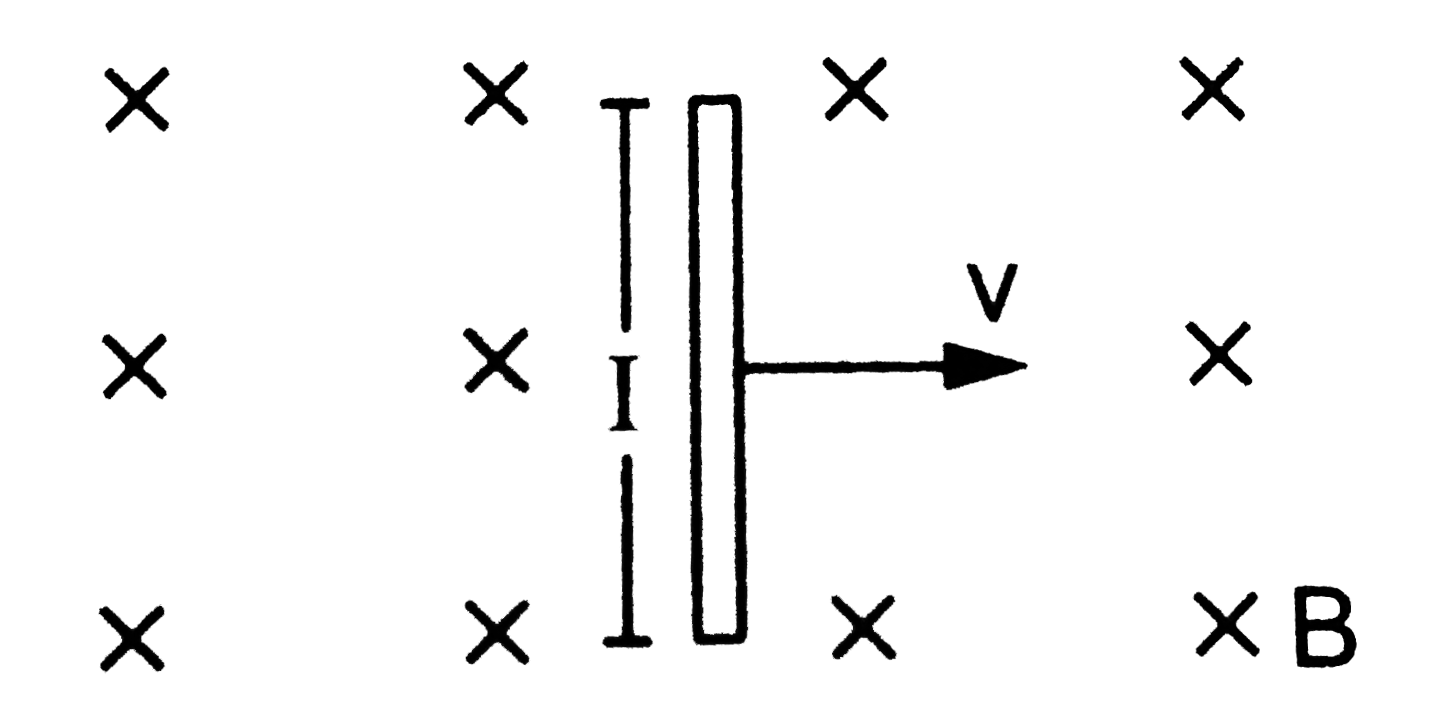
- A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, mo...
Text Solution
|
- A currrent I is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm under the action of a ma...
Text Solution
|
- A proton goes undeflected in a crossed electric and magnetic field (th...
Text Solution
|
- A particle having mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a 10 cm long portion of a straight wire carrying a current of...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 2A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side ...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagn...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length l metre carries a current I ampere along the Y-axis. ...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 10 A exists in the circuit figure.The wire PQ has a lengt...
Text Solution
|
- A thin straight horizontal wire of length 0.2 m whose mass is 10^(-4) ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x-y plane along the curve...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid wire consists of a semicircular portion of radius R and two s...
Text Solution
|
- A metal wire PQ of mass 10 gm lies on two horizontal metal rails separ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field existing in a region is given by B=B(0)(1-x/y)hatk,...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel wires separated by a distance of 10cm carry currents of 1...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a part of an electric circuit. The wires AB, CD, and EF a...
Text Solution
|
- A straight , long wire carries a current a current of 20A. Another wir...
Text Solution
|