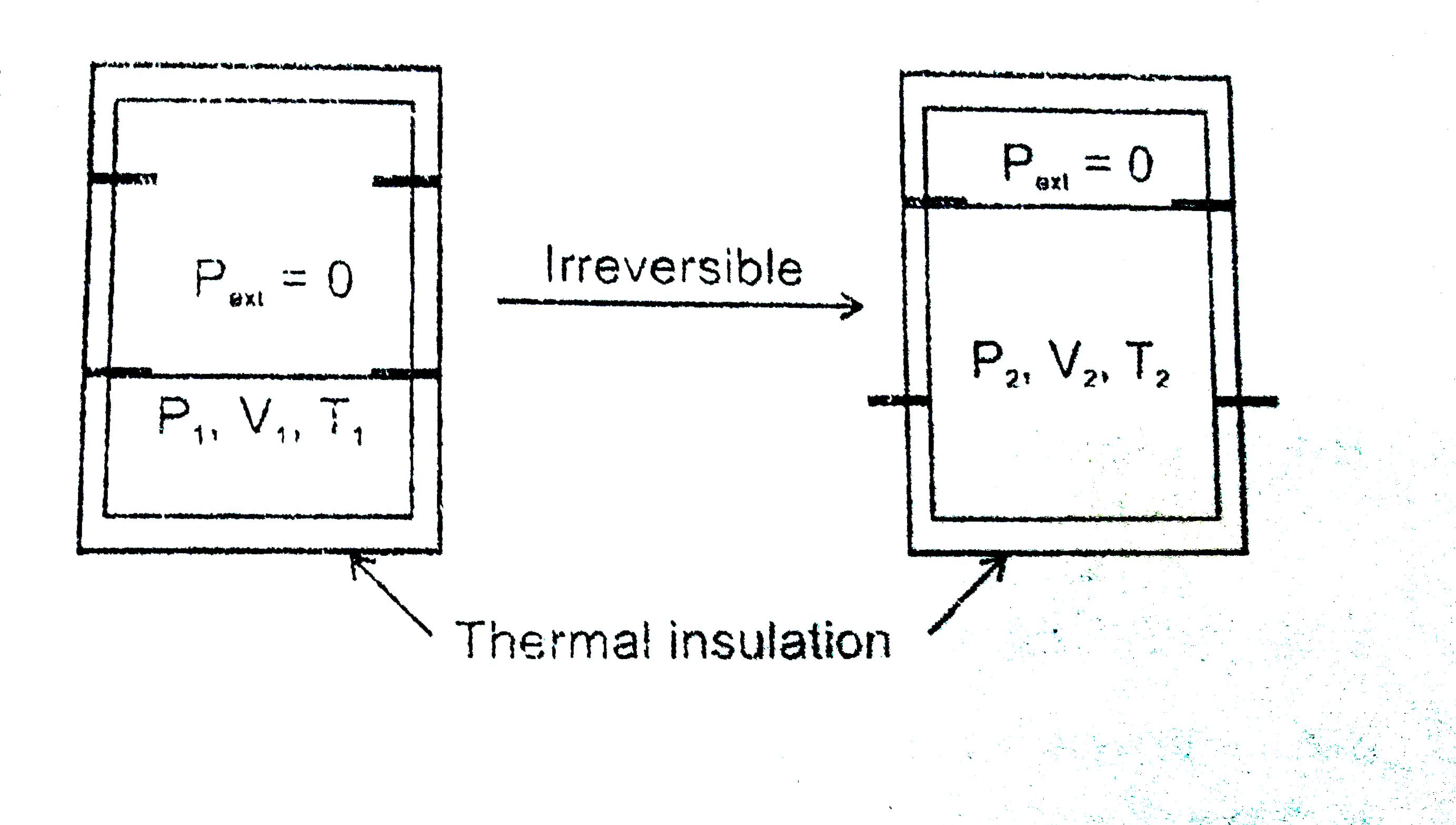A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercise-3 Part-1: JEE (ADVANCED)
- The molar heat capacity , C(v) of helium gas is 3//2R and is independe...
Text Solution
|
- 2 moles of ideal gas is expanded isothermally & reversibly from 1 litr...
Text Solution
|
- There is 1 mol liquid (molar volume 100 ml) in an adiabatic container ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas at temperature T and volume 1L exp...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of P to V at any instant is constant and is equal to 1, for ...
Text Solution
|
- The given reaction underset(2"moles")(2CO)+underset(1"mole")(O(2))ra...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the intensive property is (properties are):
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the intensive property is (properties are):
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas is taken from a and b along two paths denoted...
Text Solution
|
- The reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isotherma...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =P(1...
Text Solution
|