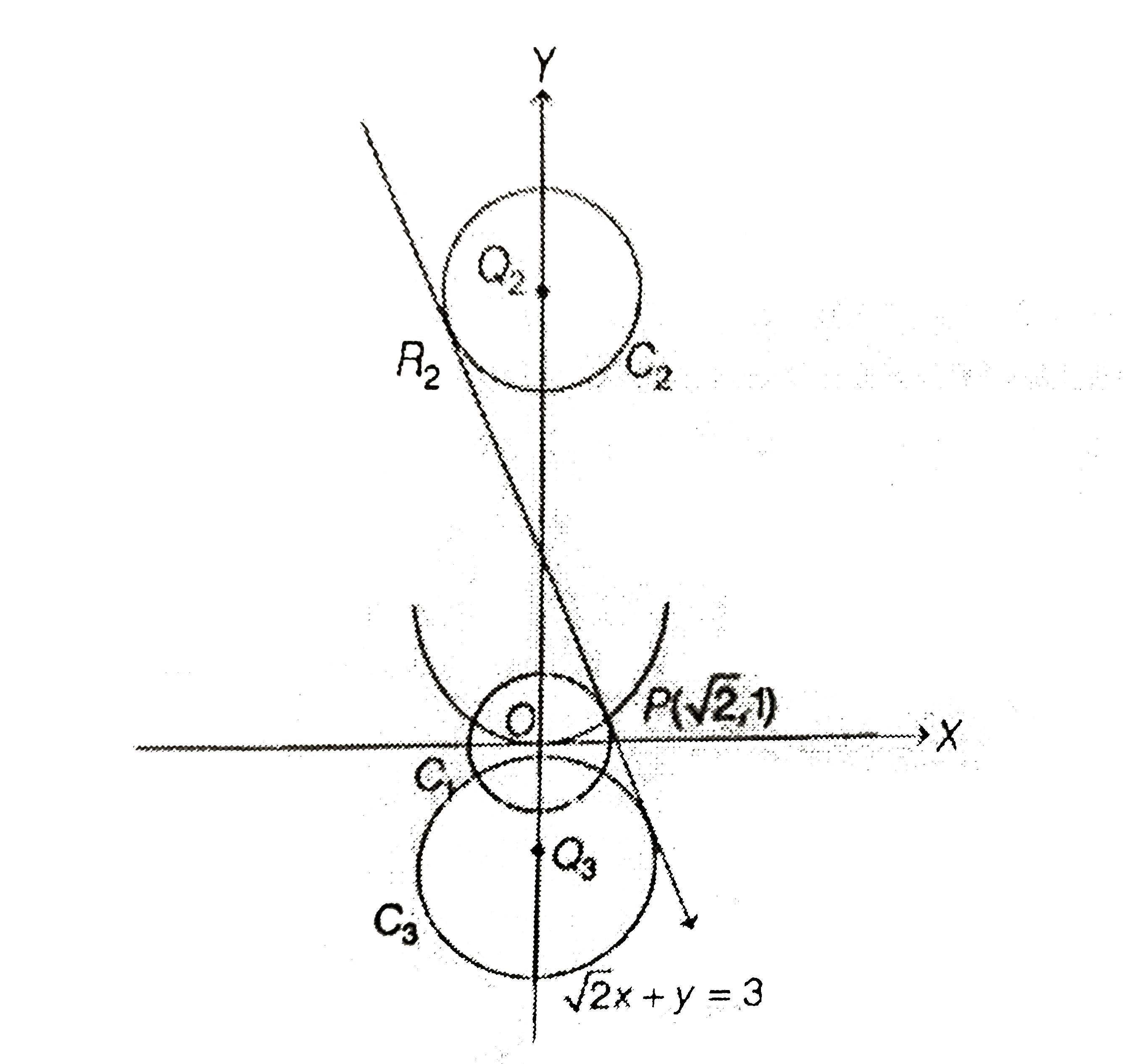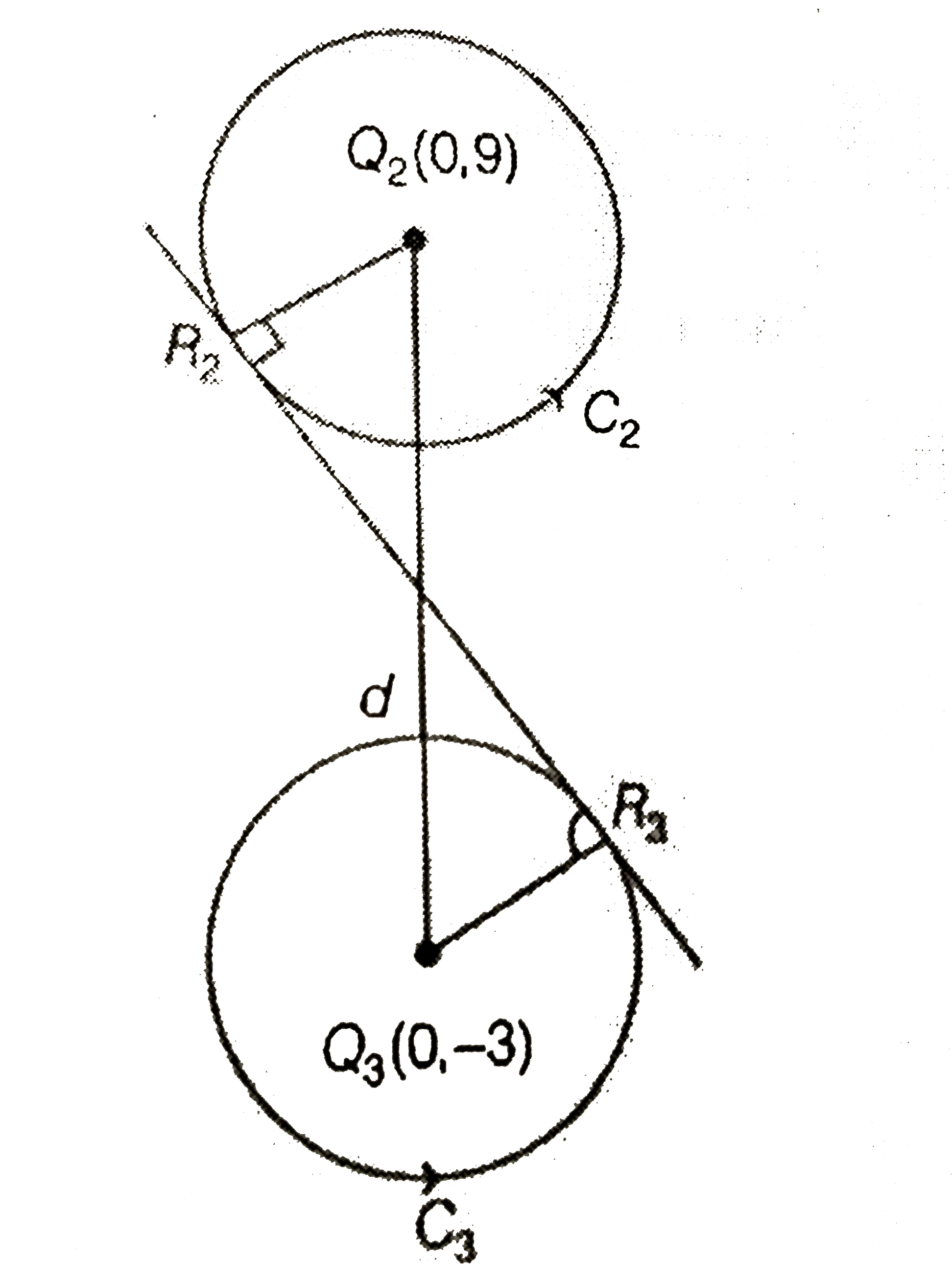A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 3 Assertion and Reason|1 VideosCIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 3 Passage Based Problems (passage 1)|3 VideosCIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 3 Equation of Tangent, Normal and Length of Tangents|9 VideosBINOMIAL THEOREM
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 2 Properties of Binomial Coefficent Objective Questions I (Only one correct option) (Analytical & Descriptive Questions )|8 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise TOPIC 5 DE-MOIVRES THEOREM,CUBE ROOTS AND nth ROOTS OF UNITY (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTION)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems