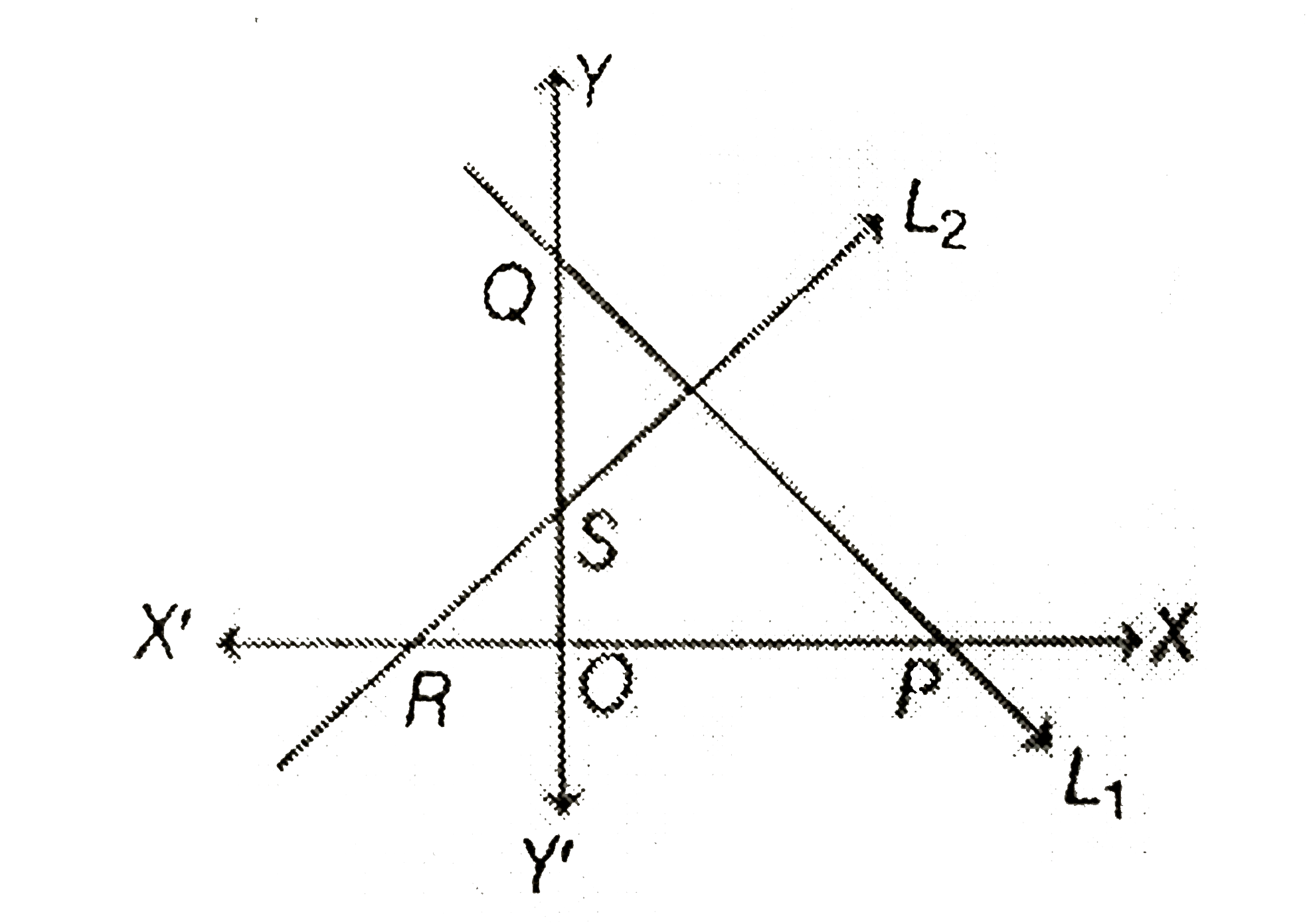Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 5 (objective Questions I)|6 VideosCIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 5 (objective Questions II)|1 VideosCIRCLE
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 4 Fill in the blanks|4 VideosBINOMIAL THEOREM
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Topic 2 Properties of Binomial Coefficent Objective Questions I (Only one correct option) (Analytical & Descriptive Questions )|8 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise TOPIC 5 DE-MOIVRES THEOREM,CUBE ROOTS AND nth ROOTS OF UNITY (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTION)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IIT JEE PREVIOUS YEAR-CIRCLE-Topic 4 Analytical & Descriptive Questions
- Consider the family ol circles x^2+y^2=r^2, 2 < r < 5 . If in the fir...
Text Solution
|
- A family of circles passing through the points (3, 7) and (6, 5) cut t...
Text Solution
|
- A circle touches the line y = x at point P such that OP = 4 sqrt2, Cir...
Text Solution
|
- Let S-=x^2+y^2+2gx+2f y+c= be a given circle. Find the locus of the fo...
Text Solution
|
- Let a given line L1 intersect the X and Y axes at P and Q respectively...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equations of the circles passing through the point (-4,3) and...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of a circle which passes through the point (2,0) ...
Text Solution
|