Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-[Set-III]
- Justify that electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the direction of induced current in metal rings 1 and 2 when c...
Text Solution
|
- The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Iden...
Text Solution
|
- Define mutual inductance between two long coaxial solenoids. Find out ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop of wire of size 2.5 cm xx 4 cm carries a steady cur...
Text Solution
|
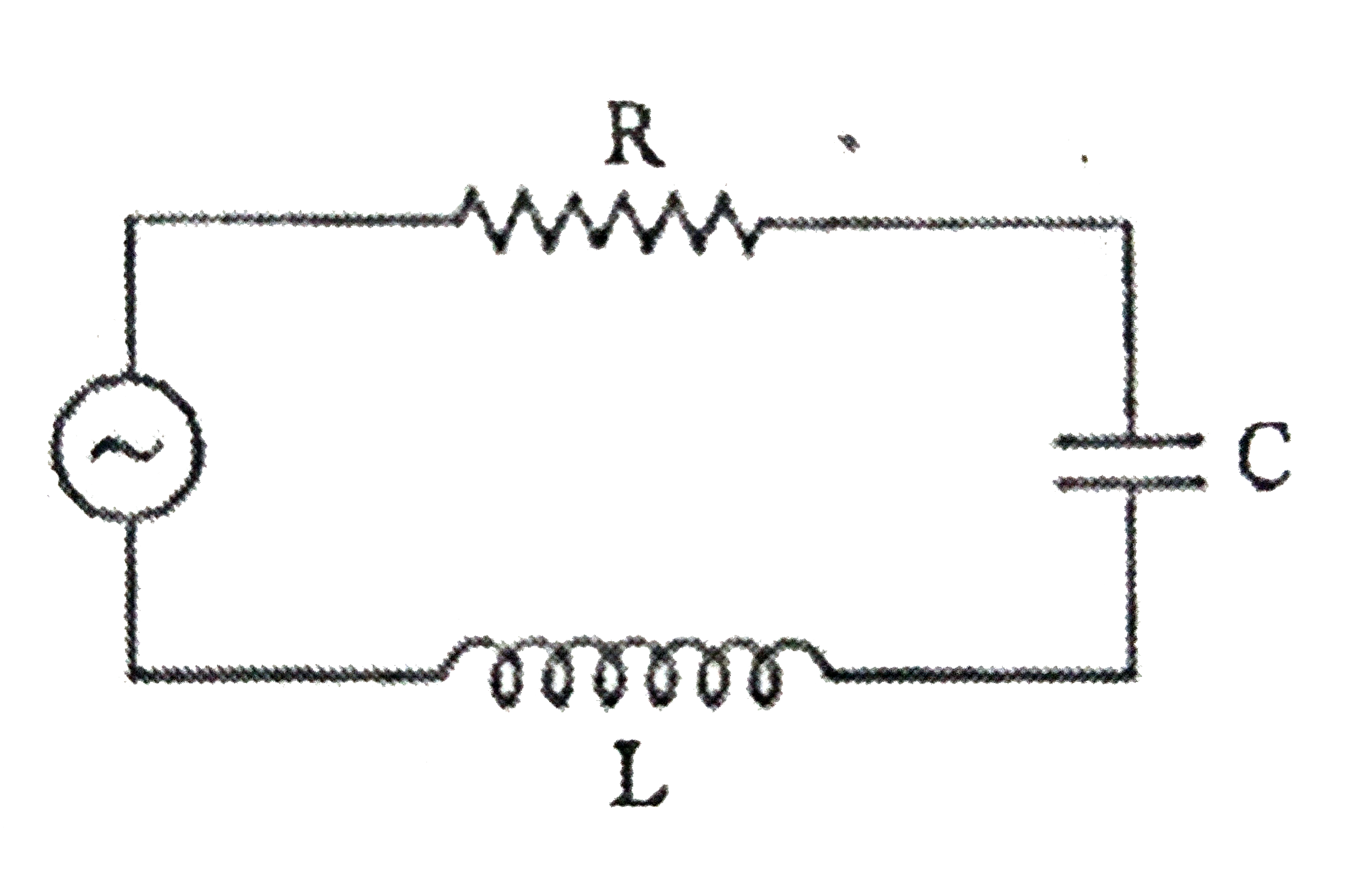
- The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L=10.0 H(2), C=40 mu F, R=6...
Text Solution
|