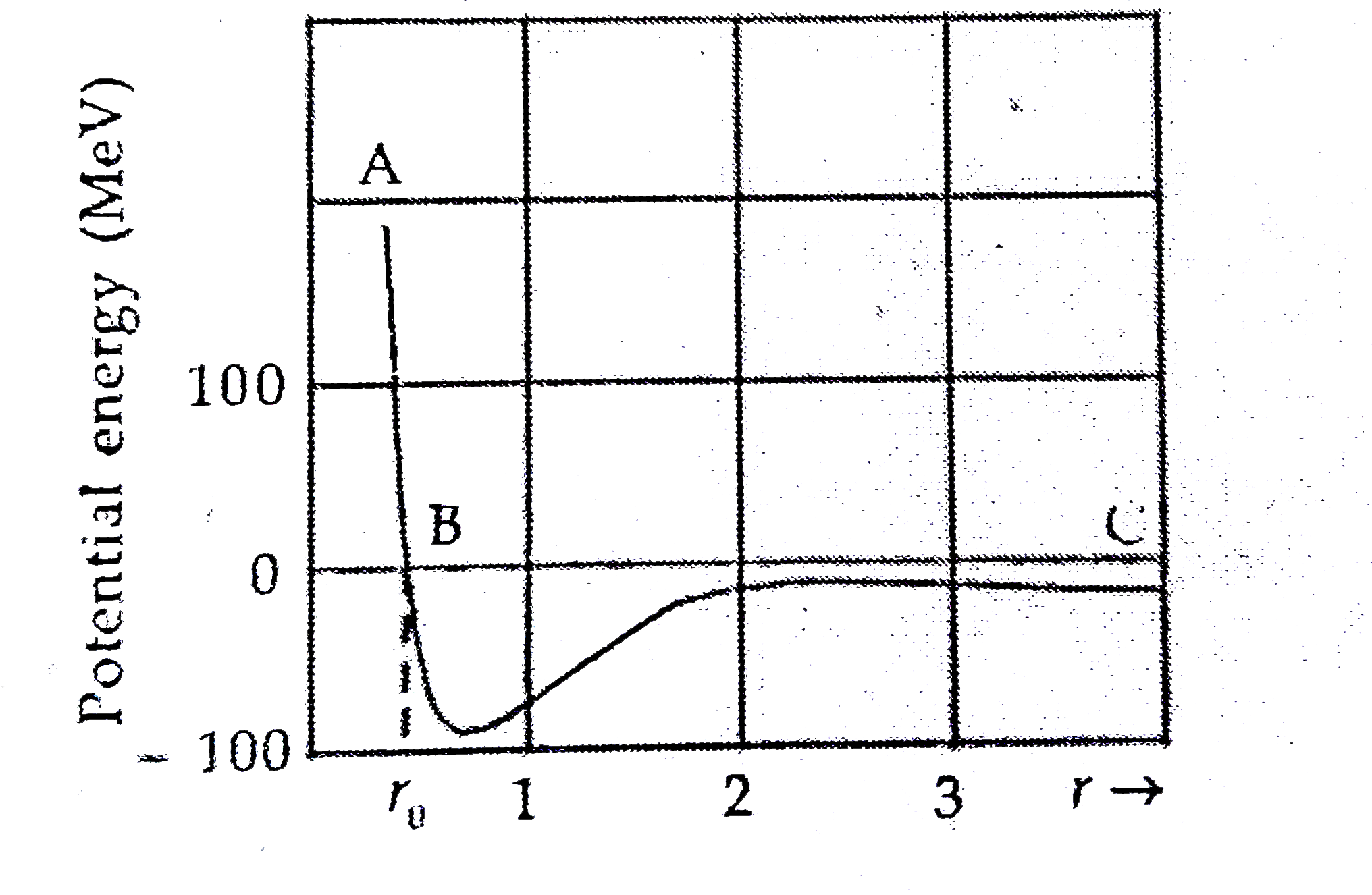
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SET - III (Delhi Board)
- A 5 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following substances are para-magnetic? Bi, Al, Cu, Pb,...
Text Solution
|
- An ammeter of resistance 0.6Omega can measure current upto 1.0 A. Calc...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is placed coaxially in contact wit...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a battery of V ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow cylindrical box of length 0.5m and area of cross-section 20cm...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write two characteristics features distinguishing the diffraction...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In a nuclear reaction ""(2)^(3)He +""(2)^(3)He to ""(2)^(4)He+""(...
Text Solution
|