Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-[SET - I]
- Identify the logic gates marked P and Q in the circuit Fig. Write the ...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor C, a variable resistor R and a bulb B are connected in ser...
Text Solution
|
- A proton and deutron are accelerated through the same accelerating pot...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Mono chromatic light of frequency 6.0xx10^(14)Hz is produced by a ...
Text Solution
|
- A 12/5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room te...
Text Solution
|
- When Sunita, a class XII student, came to know that her parents are pl...
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 10Omega. It is ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the formation of a final image...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A mobile phone lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror. ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How is a toroid different from a solenoid? (b) Show that in an i...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the magnetic moment (vec mu) of an electron r...
Text Solution
|
- (a) State Ampere's circuital law, expressing it in the integral form. ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following : (a) Name the em waves which are suitable for ...
Text Solution
|
- Deduce the expression, N=N(0)^(-lambdat) for the law of radioactive de...
Text Solution
|
- (a) (i) Two independent mono chromatic sources of light cannot produc...
Text Solution
|
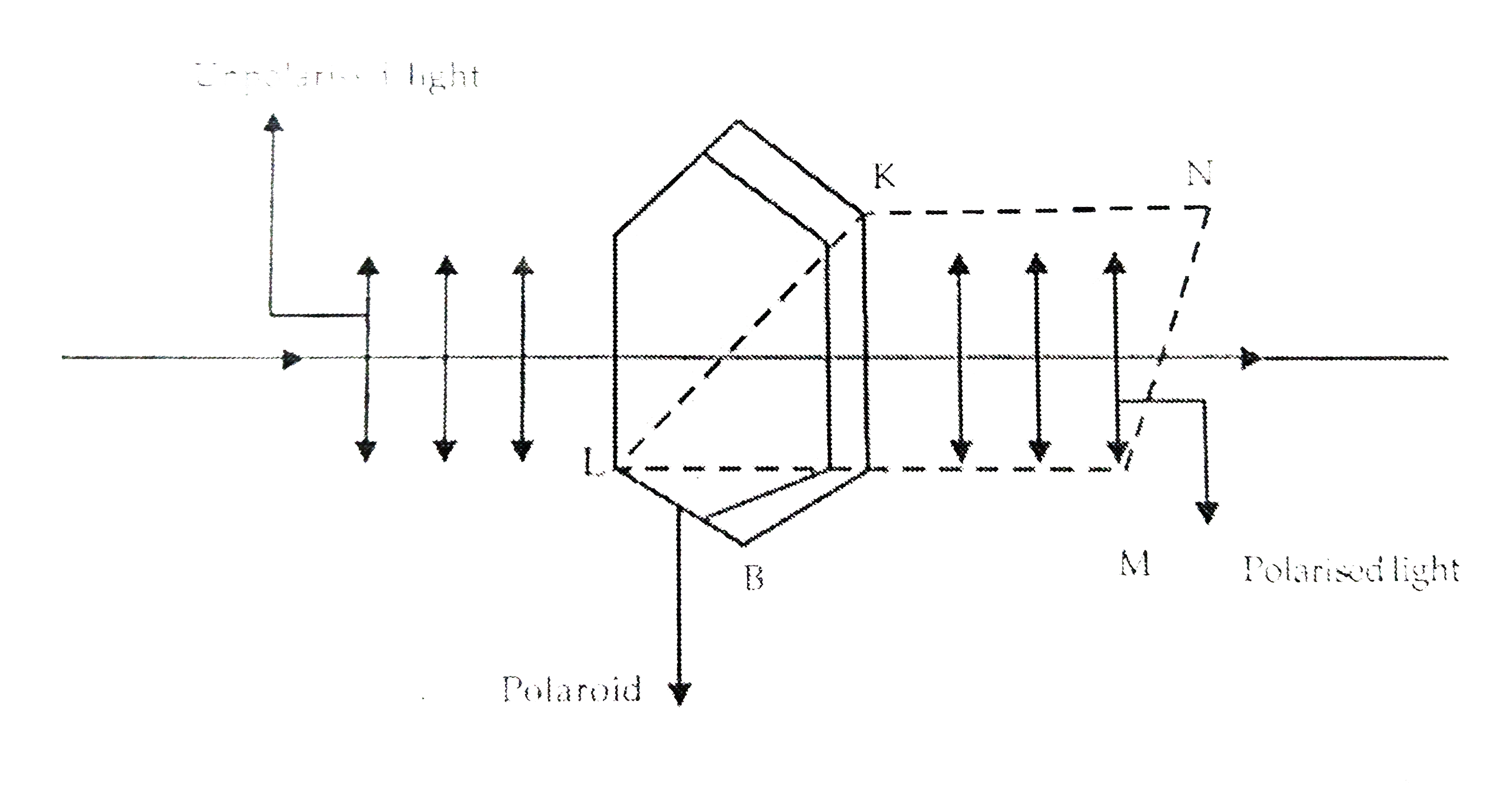
- (a) How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolaris...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Describe a simple experiment (or activity) to show that the polari...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a schematic sketch of an generator describing its basic elements....
Text Solution
|
- Using the necessary circuit diagram, show how the V-I characteristics ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Differentiate between three segments of a transistor on the basis ...
Text Solution
|