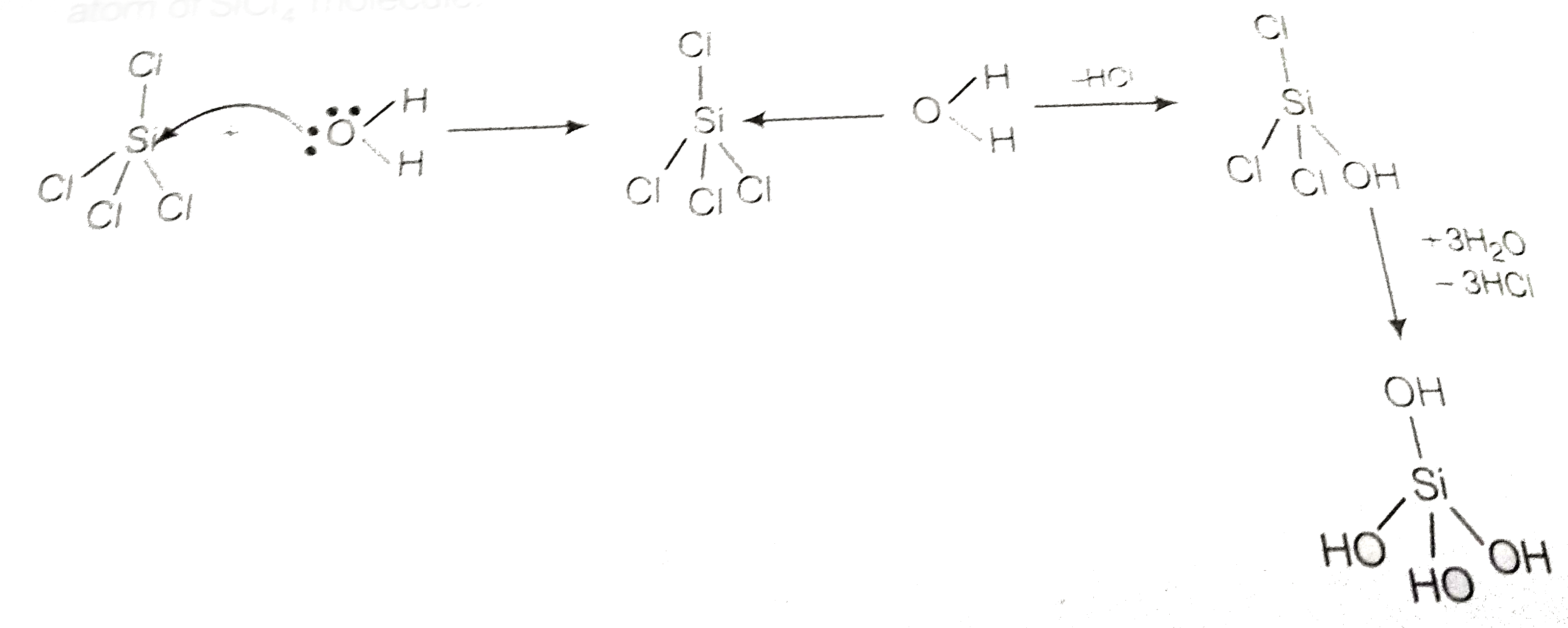
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Matching|3 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion and Reason|2 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer|9 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise All Questions|55 VideosTHE S-BLOCK ELEMENTS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer Type Questions|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-THE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS-Short Answer
- Draw the structures of BCl(3).NH(3) and AlCl(3) (dimer).
Text Solution
|
- Explain the nature of boric acid as a Lewis acid in water.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structure of boric acid showing hydrogen bonding. Which speci...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids ? (a) BCl(...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following (a) C Cl(4) is immiscible in water, w...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following (a) CO(2) is a gas whereas SiO(2) is a solid ...
Text Solution
|
- The +1 oxidation state in group 13 and +2 oxidation state in group 14 ...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon and silicon both belong to the group 14, but inspite of the sto...
Text Solution
|
- If a trivalent atom replaces a few silicon atoms in three dimensional ...
Text Solution
|
- When BCl(3) is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH](4)]^...
Text Solution
|
- Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus sho...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following (a) Gallium has higher ionisation enthalpy tha...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the compounds A,X and Z in the following reactions A+2HCl+5...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical equations Z+3LiAlH(4)rarrX+3LiF+3AlF...
Text Solution
|