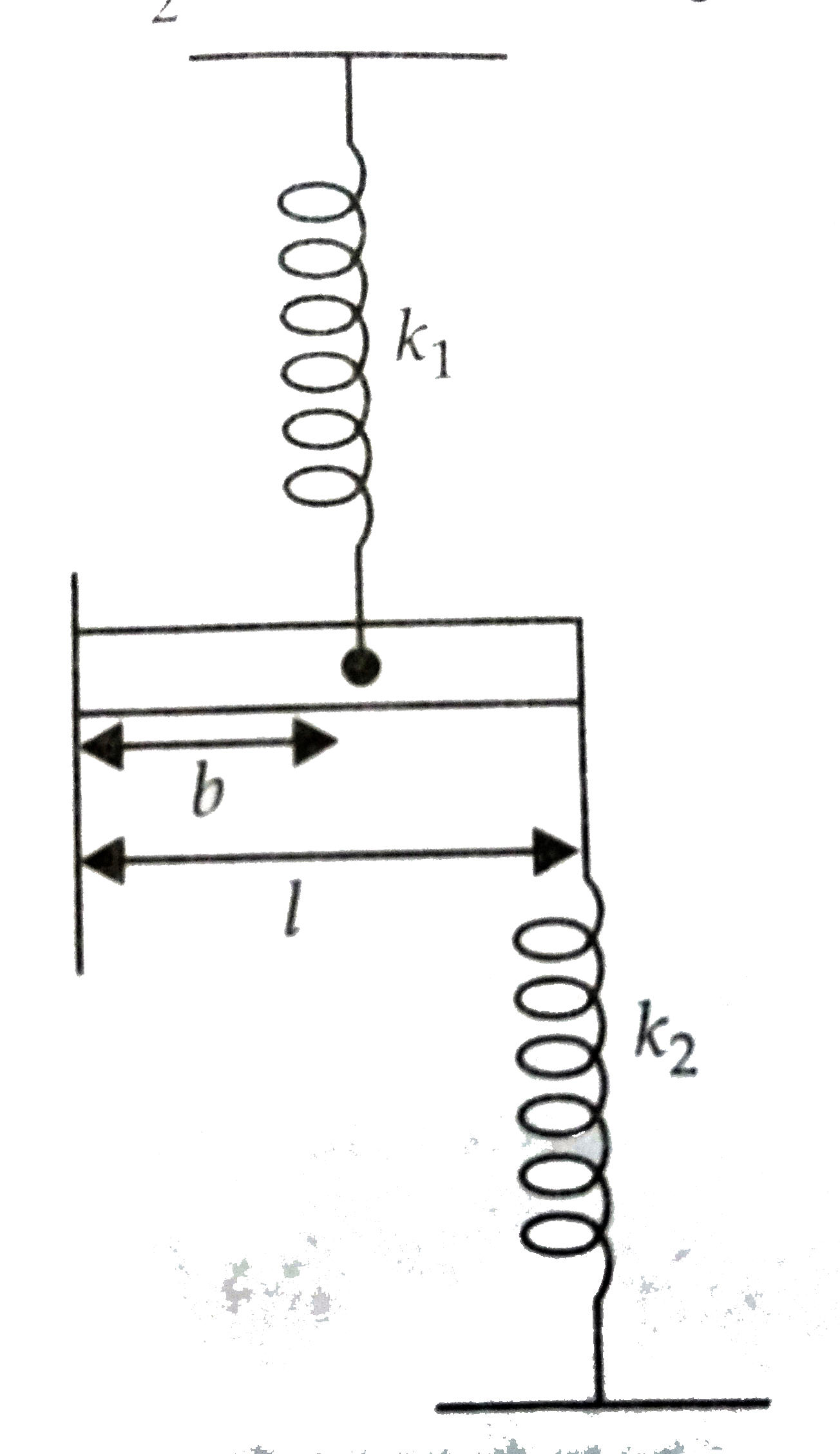
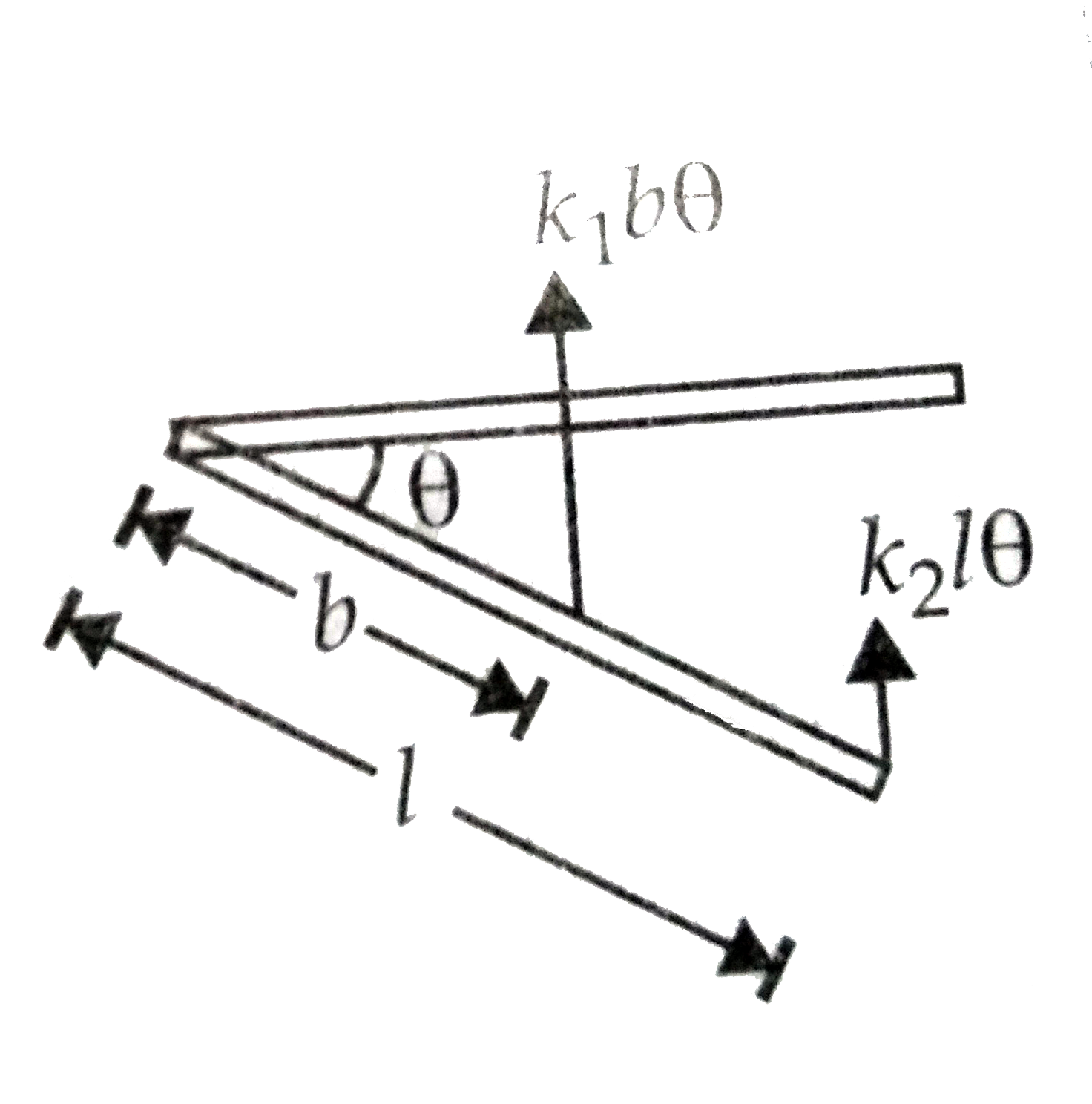
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Exemplar Problems|9 VideosOSCILLATIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion & Reason|15 VideosOSCILLATIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|6 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-OSCILLATIONS -Higher Order Thinking Skills
- An ideal gas enclosed in a cylindrical container supports a freely mov...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length l and mass M is pivoted at the centre. Its two...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar with mass m lies symmetrically across two rapidly rotati...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum has a string of length 99.39 cm. how much length of the pen...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length l is connected by two spring of spring cons...
Text Solution
|
- A spring is loaded with two blocks m(1) and m(2), where m(1) is rigidl...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles execute SHM of same amplitude and same time period, abou...
Text Solution
|
- A particle executes S.H.M. between x = -A and x = + A. The time taken ...
Text Solution
|