A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
JEE MAIN 2021
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise SECTION-B|40 VideosJEE MAIN 2021
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise PHYSICS (SECTION-A)|20 VideosJEE MAIN 2021
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise PHYSICS SECTION B|30 VideosJEE MAIN
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise All Questions|473 VideosJEE MAIN 2022
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR|Exercise Question|492 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR-JEE MAIN 2021-SECTION-A
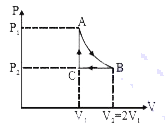
- n mole a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) cons...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the sphe...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, the width of the one of the slit ...
Text Solution
|
- Two stars of masses m and 2m at a distance d rotate about their common...
Text Solution
|
- A current through a wire depends on time as i = alpha0 t + beta t^2 w...
Text Solution
|
- Moment of inertia (M.I.) of four bodies, having same mass and radius, ...
Text Solution
|
- Given below are two statements : Statement-I : Two photons having e...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, a mass M is attached to a horizontal spring which...
Text Solution
|
- If Y, K and eta are the values of Young's modulus, bulk modulus and m...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure the energy levels of hydroge atom have been sh...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical particles of equal masses 1kg made to move along the ci...
Text Solution
|
- If the velocity-time graph has the shape AMB, what would be the shape ...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal capacitors are first connected in series and then in paralle...
Text Solution
|
- If an emitter current is changed by 4 mA, the collector current change...
Text Solution
|
- Match List-I with List-II:
Text Solution
|
- Each side of a box made of metal sheet in cubic shape is 'a' at room t...
Text Solution
|
- A cell E1 of emf 6V and internal resistance 2Omega is connected with a...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of side 'a' has point charges +Q located at each of its vertice...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two satellites S1 and S2 with periods of revolution 1 hr. an...
Text Solution
|
- The workdone by a gas molecule in an isolated system is given by, W = ...
Text Solution
|