Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OSWAAL PUBLICATION-SOLVED PAPER II PUC JULY - 2016-PART -E
- Explain S(N)2 mechanism taking an example of chloromethane.
Text Solution
|
- Write the general equation for the reaction of primary alcohol with SO...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)Br + AgF rarr CH(3)F + AgBr. Name the reaction.
Text Solution
|
- p-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than those of ortho and met...
Text Solution
|
- i) Identifiy 'A' and 'B' in the following equations. CH(3)-CH=CH(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- What is Lucas reagent ? How it is used to identify secondary alcohols?
Text Solution
|
- Explain Williamson's ether synthesis.
Text Solution
|
- i) How does benzaldehyde reacts with acetophenone in presence of a dil...
Text Solution
|
- i) How does benzaldehyde reacts with acetophenone in presence of a dil...
Text Solution
|
- Among formic acid and acetic acid, which is more acidic ? Give reason...
Text Solution
|
- i) Explain the reduction of nitrocompounds to amines with an examples....
Text Solution
|
- i) Explain the reduction of nitrocompounds to amines with an examples....
Text Solution
|
- How is aniline converted in phenyl isocyanide ? Write the equation.
Text Solution
|
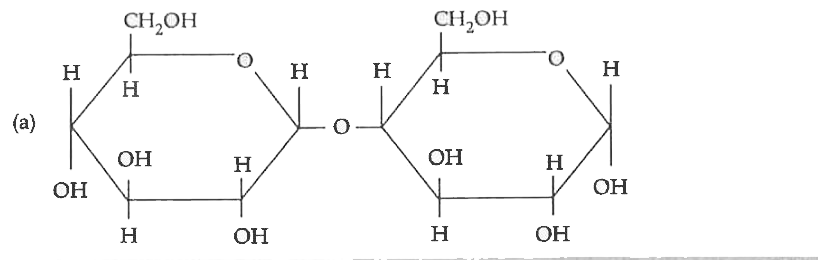
- Write Haworth structure for maltose.
Text Solution
|
- What is nucleoside?
Text Solution
|
- What are fibrous proteins Give an example .
Text Solution
|
- Name the monomers usedl in the manufacture of Nylon-6, 6.
Text Solution
|
- What is vulcanisation of rubber?
Text Solution
|
- Give an example for biodegradable polymer.
Text Solution
|