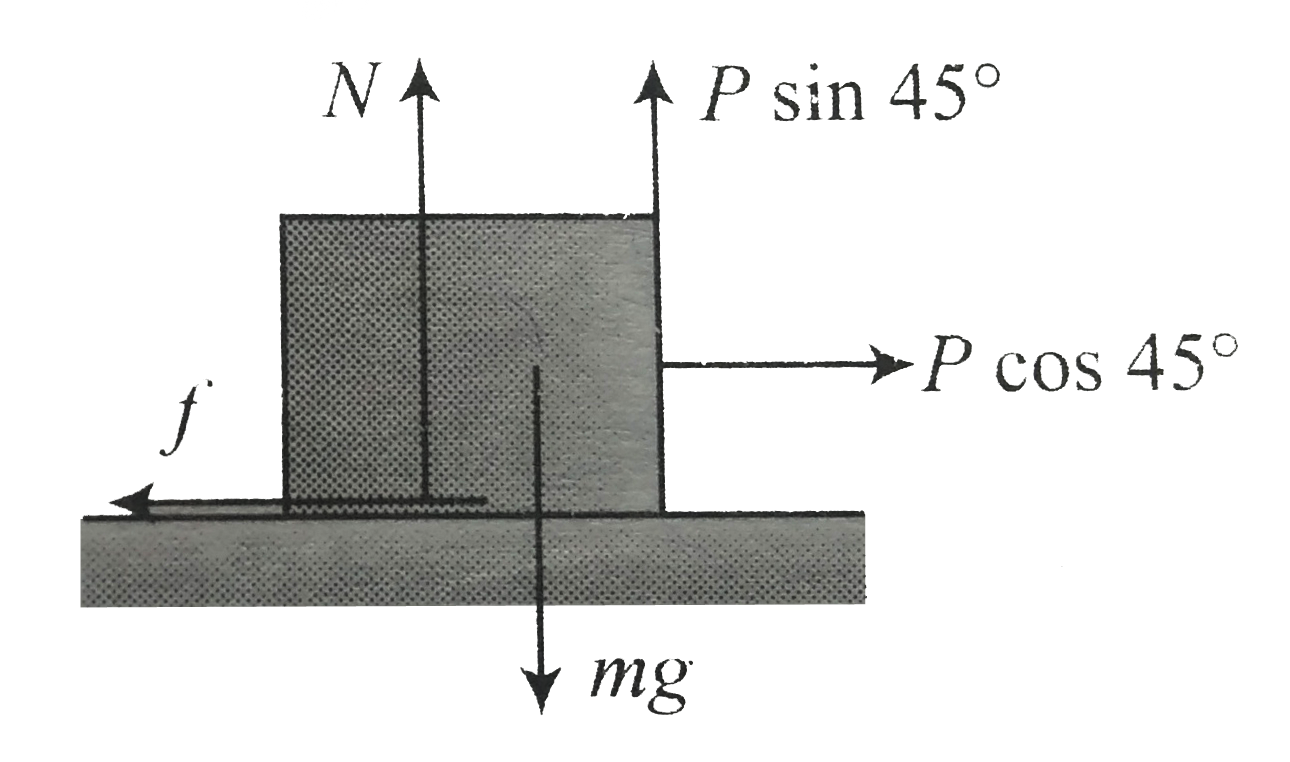
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|12 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 7.1|25 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|5 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems