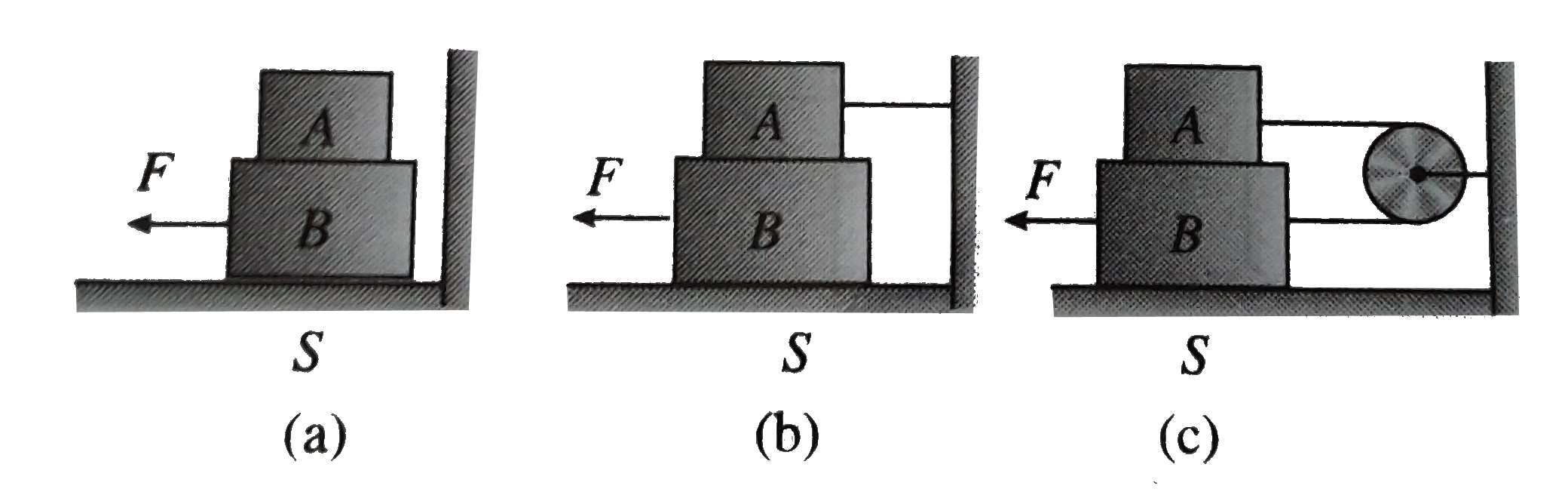
Block A weight `4N` and block B weight `8N` The coefficient of kinetic friction is `0.25` for all surface. Find F to slide B at constant speed when
A is held at rest
Block A weight `4N` and block B weight `8N` The coefficient of kinetic friction is `0.25` for all surface. Find F to slide B at constant speed when

A is held at rest

A is held at rest
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
a. If block `A and B` move together , the friction between `A and B` is static and friction between `B` and ground will be of kinetic nature.
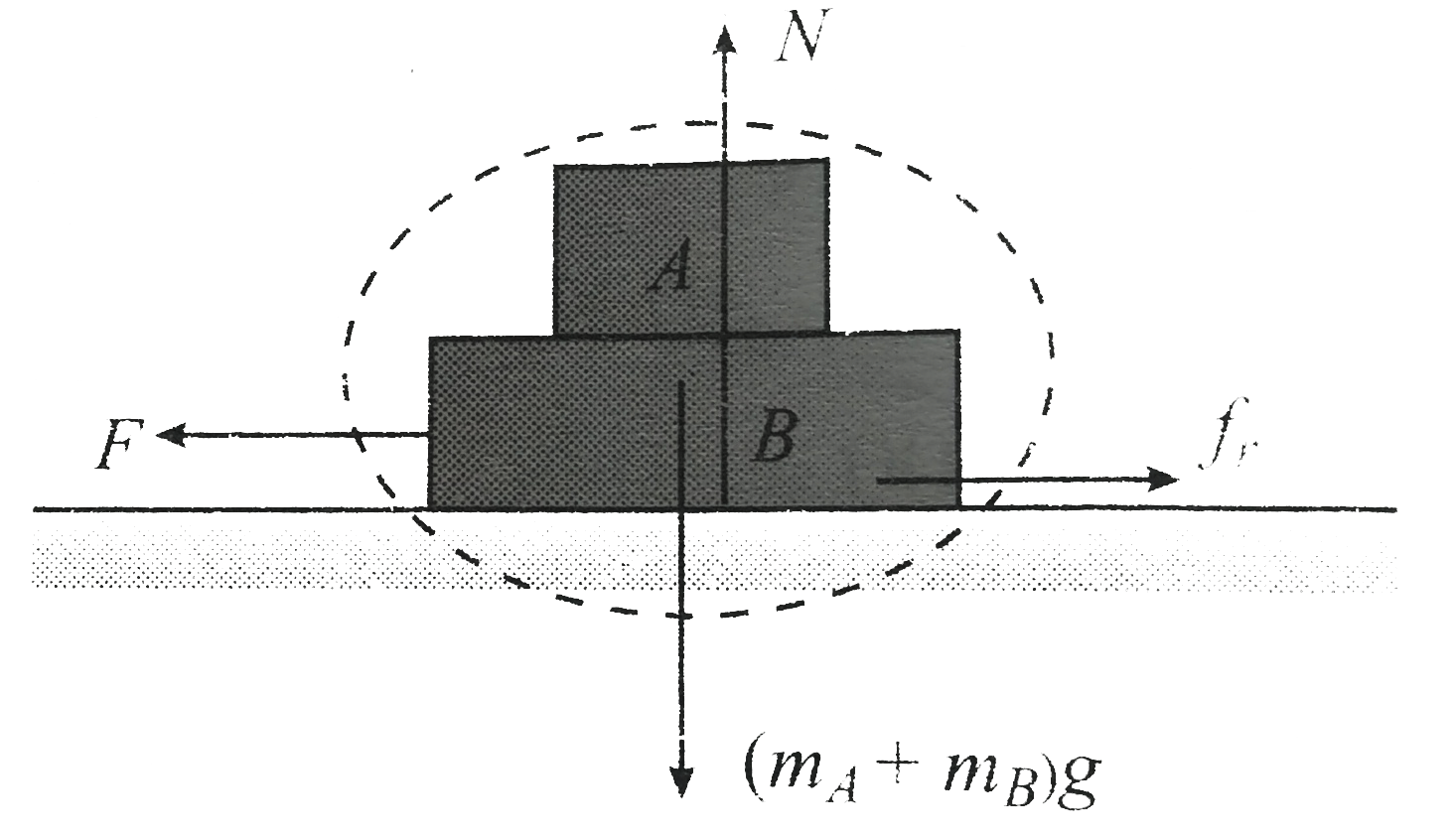
`FBD` of `A +B` For `A and B` both move with constant velocity , the net force acting on the system of `A + B` should be zero
`F = f_(r) = mu N = mu(m_(A) + m_(B)) g`
b . If `A` is held at rest , The friction force on top and bottom surface of block `B` will be kinetic
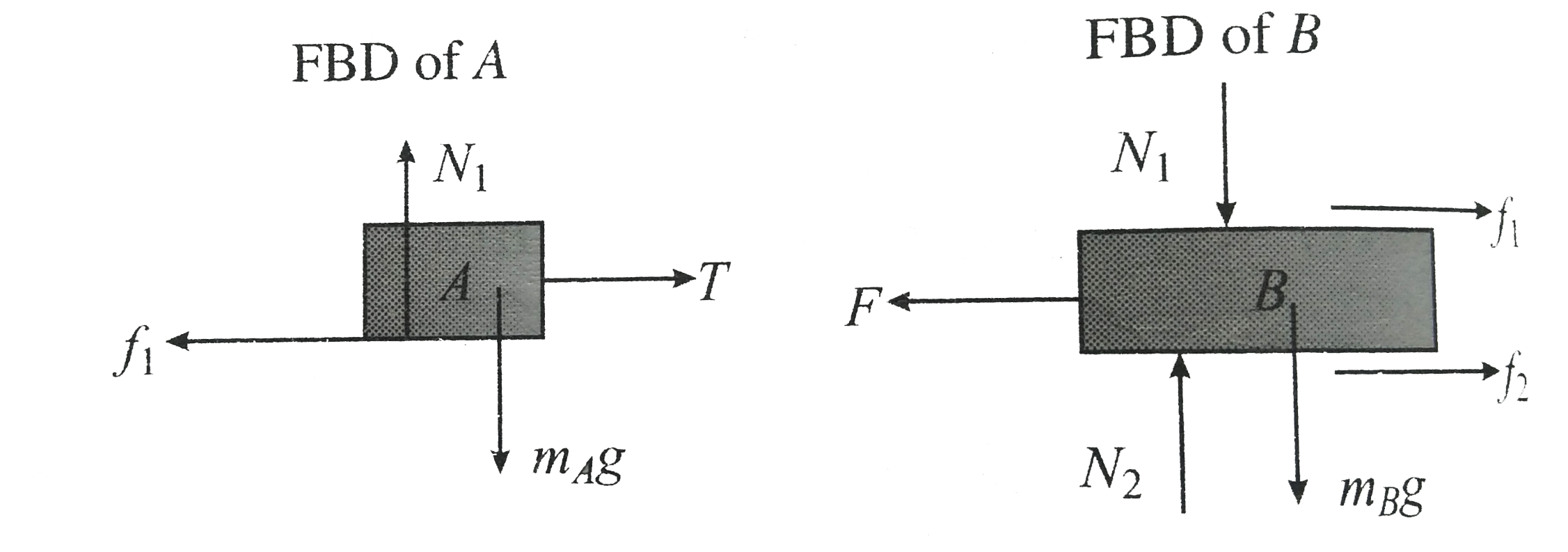
Friction at the top surface of block `B`
`f_(1) = mu N_(1) = mu m _(A)g`
Friction at the bottom surface of block `B`
`f_(2) = mu N_(2) = mu (m _(A) + m_(B))g`
If block `B` moves with constant speed .
`F = f_(1) + f_(2) = mu m _(A)g + mu(m _(A) + m_(B))g`
`F = mu (2m_(A) + m_(B))A`
c. Now `A and B` are connected by light string .If force block `B` block `B` will move toward left block `A and B` are connected by string block `A` move toward right .The direction of friction force be opposite to relation motion and is shown in fig
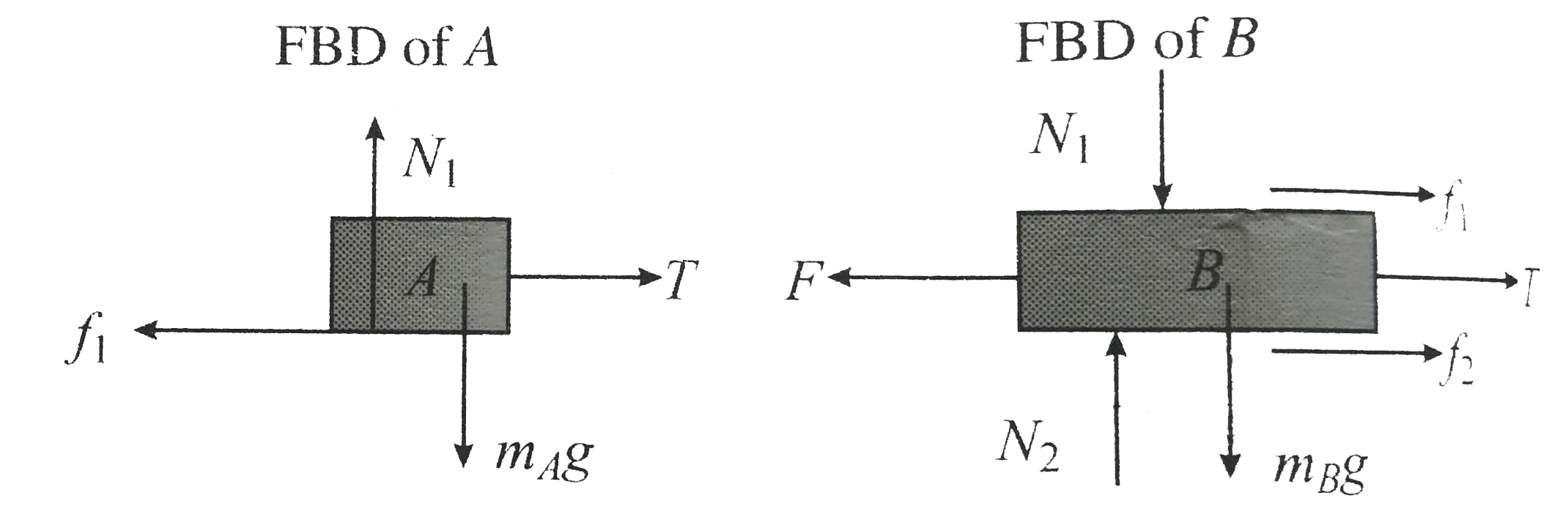
From `FRD` of `A : T = f_(1) = mu N_(1) = mu m_(A)g`
From `FBD` of `B : F = f_(1) - f_(2) + T`
` = 2f_(1) + f_(2)`
`= 2 mu m_(A)g + mu (m_(A) + m_(B))g`
`rArr F = mu (3m_(A) + m_(B))A`
`FBD` of `A +B` For `A and B` both move with constant velocity , the net force acting on the system of `A + B` should be zero
`F = f_(r) = mu N = mu(m_(A) + m_(B)) g`

b . If `A` is held at rest , The friction force on top and bottom surface of block `B` will be kinetic

Friction at the top surface of block `B`
`f_(1) = mu N_(1) = mu m _(A)g`
Friction at the bottom surface of block `B`
`f_(2) = mu N_(2) = mu (m _(A) + m_(B))g`
If block `B` moves with constant speed .
`F = f_(1) + f_(2) = mu m _(A)g + mu(m _(A) + m_(B))g`
`F = mu (2m_(A) + m_(B))A`
c. Now `A and B` are connected by light string .If force block `B` block `B` will move toward left block `A and B` are connected by string block `A` move toward right .The direction of friction force be opposite to relation motion and is shown in fig

From `FRD` of `A : T = f_(1) = mu N_(1) = mu m_(A)g`
From `FBD` of `B : F = f_(1) - f_(2) + T`
` = 2f_(1) + f_(2)`
`= 2 mu m_(A)g + mu (m_(A) + m_(B))g`
`rArr F = mu (3m_(A) + m_(B))A`
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|12 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 7.1|25 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|5 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Block A weighs 4 N and block weigh 8 N The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25 for all surface find the force F to slide B at a constant speed when (a) A rest on B and moves with it (b) A is held at rest and (c ) A and B are connected by a light cord passing over a smooth putting as shown in fig 7.31 (a - c) restively.
Block A as shown in figure weight 1.40 N and block B weight 4.20 N The coefficient of kinetic friction between all surface is 0.30 Find the magnitude of the horizontal force necessary to drag block B to the left at constant speed if A and B are connected by a light , fiexible cort passing around a fixed , frictionless pulled.
Block A as shown in Fig weighs 2.0 N and block B weighs 6.0 N The coefficient of ikinetic friction between all surface is 0.25 Find the magnitude of the horizontal force necessary to drag block B to the left at constant speed if A and B are connected by a light , flxeible cord passing around a fixed, frictionless pulley
Two blocks are connected over a massless pulley as shown in figure. The mass of block A is 10 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2 Block A sliders down the incline at constant speed. The mass of block B in kg is
Block A has a weight of 300 N and block B has a weight of 50 N . Coefficient of friction for A is mu_(k) = 0.2 . Determine the speed of block A after moves 1 m down the plane, starting from rest. Negelect the mass of the cord and pulleys.
a. Block A , as shown in figure weight 60.0 N The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface on which it rest is 0.25 .The waight w is 12N The system is in equlibrium .Find the friction for excerted on block A b. Find the maximum weight w for which the system will remain in equlibrium
Blocks A, B and C are placed as shown in Fig and connected by the rops of negligible mass . Both A and B weigh 25.0 N each , and the coefficient of kinetic friction between each and the surface is 0.35 blocks C descends with constant velocity . a. Draw two separate free- body diagrams showing the forces acting on A and B b. Find the tension in the rope connecting blocks A and B c. What is the weight of blocks C? d. If the rope connecting A and B were cut, what would be the acceleration of C?
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface. A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration (F)/(2(m+M)) in the sytem. The two blocks always move together. Consider displacement d of the system. a. Find the work done by friction on bigger block. b. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. c. Find the frictional acting on the smaller block. d. Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block. e. Find the work done by static friction on bigger block.
A block of mass 4 kg is kept on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction is 0.8. If a forace of 19 N is applied on the block parallel to the floor, then the force of friction between the block and floor is
A block A of weight W slide down an inclined plane S of slope 37^(@) at a contact velocity,while the plane B also of weight W rests on top of A The plank B is atteched by a cord to the top of plane .The coefficient of kinetic friction mu is the same between the surface A and B and between S and A Determine the value of 1//mu