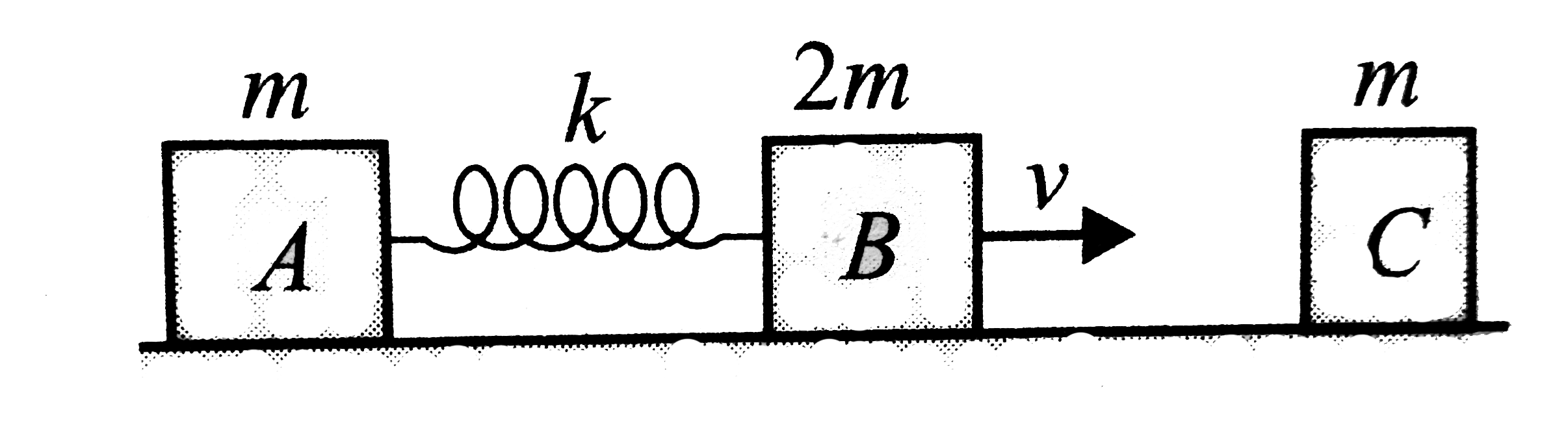Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|141 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 1.3|24 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CENTRE OF MASS-Subjective
- A stationary light, smooth pulley can rotate without friction about a ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B are joined by means of a slacked string passing ove...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m, respectively are connected by a...
Text Solution
|
- Two small spheres A and B of equal radius but different masses of 3m a...
Text Solution
|
- Four railroad cars, each of mass 2.50 xx 10^4 kg, are coupled together...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is made to move with uniform speed v along the pe...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth ball of mass 1 kg is projected with velocity 7 m//s horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is projected from point P towards a vertical wall as show...
Text Solution
|
- A small steel ball A is suspended by an inextensible thread of length ...
Text Solution
|
- A tennis ball with (small) mass m(2) rests on the top of a basketball ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m hits a wedge of mass M vertically with speed u, which...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with constant horizontal velocity u strikes a ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m collides with a stationary wedge of mass M, perpendic...
Text Solution
|
- A small bucket of mass M is attached to a long inextensible cord of le...
Text Solution
|
- Two wooden plank of mass M(1)= 1 kg, M(2) = 2.98 kg smooth surface. A ...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram shown, no friction at any contact surface. Initially, t...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of mass m and 2m respectively are moving towards a ...
Text Solution
|
- A boy throws a ball with initial speed sqrt(ag) at an angle theta to t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falls freely form a height onto and smooth inclined plane formi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected form a point A on a smooth inclined plane which ma...
Text Solution
|