A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion - Reasoning|2 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|23 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CENTRE OF MASS-Single Correct
- A ball of mass 'm' moving with speed 'u' undergoes a head-on elastic c...
Text Solution
|
- A trolley was moving horizontally on a smooth ground with velocity v w...
Text Solution
|
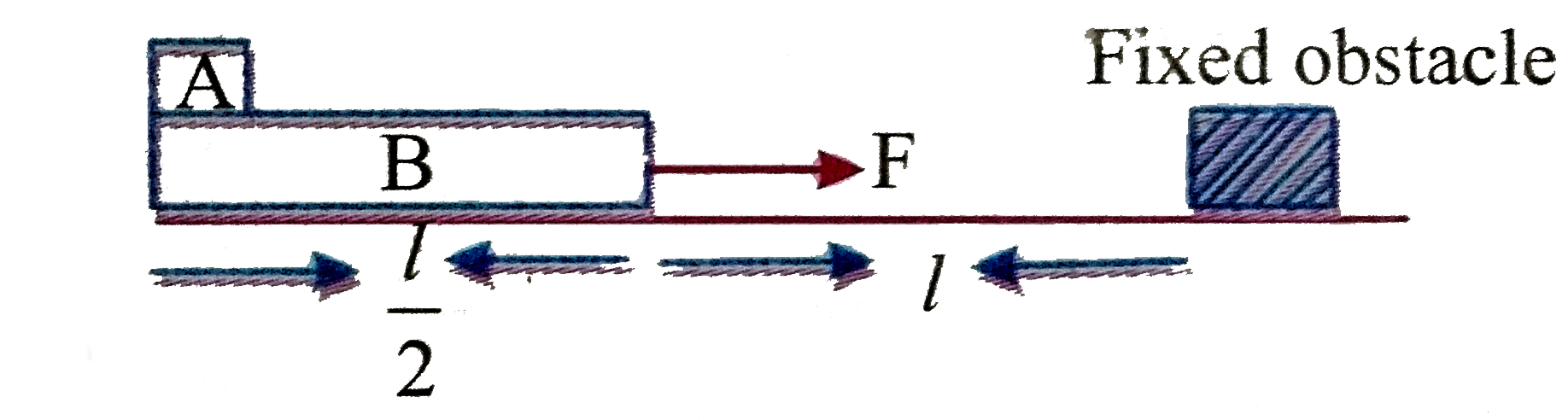
- In a figure shown mass of A and B is equal to M each. Friction between...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses in and 4m lie on a smooth horizontal surface conn...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel at rest explodes breaking it into three pieces. Two pieces ha...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary body of mass 3 kg explodes into three equal pieces. Two o...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass in collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a r...
Text Solution
|
- A body is hanging from a rigid support. by an inextensible string of l...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is let fall from a height h(0). There are n collisions with the...
Text Solution
|
- A body X with a momentum p collides with another identical stationary ...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum consists of a wooden bob of mass m and length l. A bullet o...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulums each of length l are initially situated as shown in Fig....
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block of mass 10 g is dropped from the top of a tower 100 m h...
Text Solution
|
- A machinist starts with three identical square plates but cuts one cor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2m is projected at an angle of 45^(@) with horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere is moving with velocity vector 2hati+2hatj immediately before...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal spheres A and B lie on a smooth horizontal circular groove a...
Text Solution
|
- A block 'A' of mass m1 hits horizontally the rear side of a spring (id...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 4m is projected from the ground at some angle with ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is tied to one end of a massless rope. The other end...
Text Solution
|