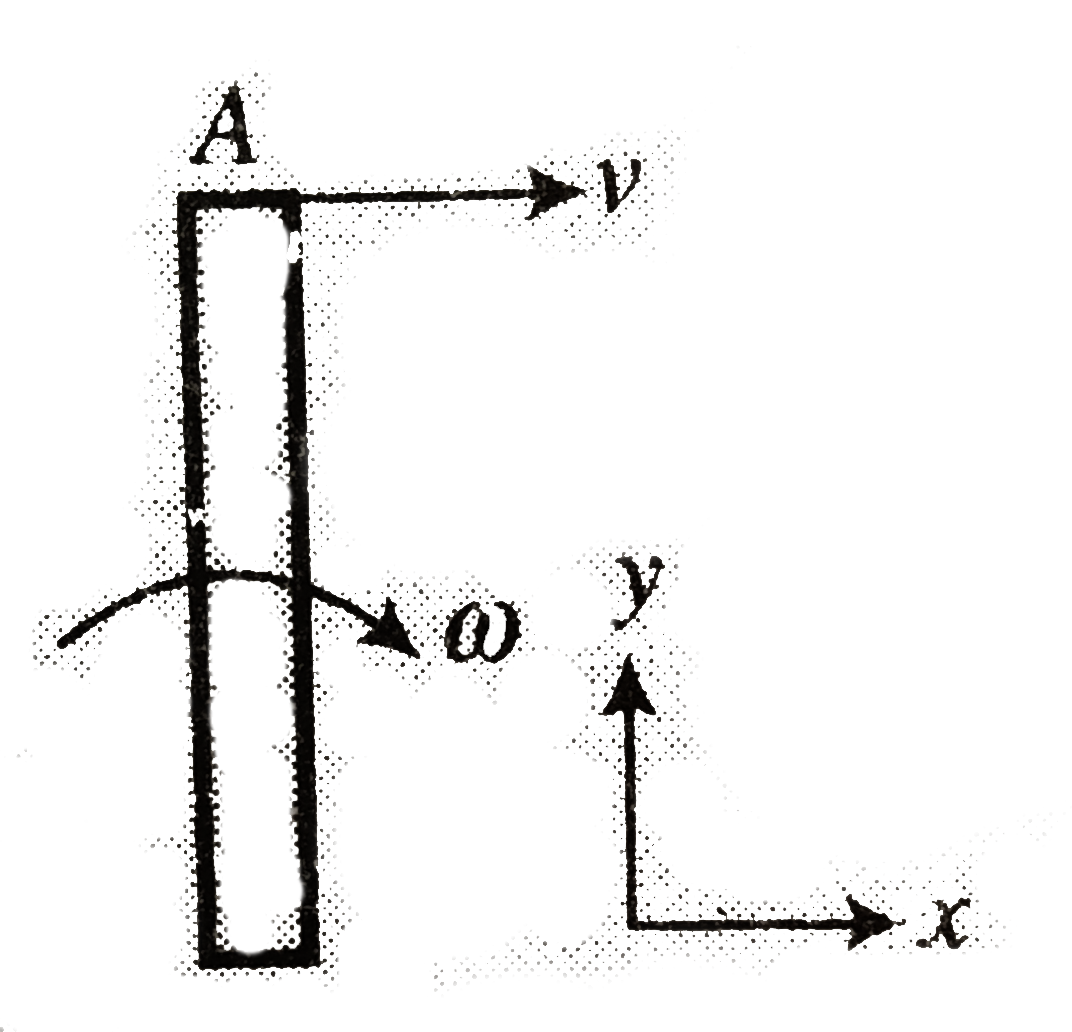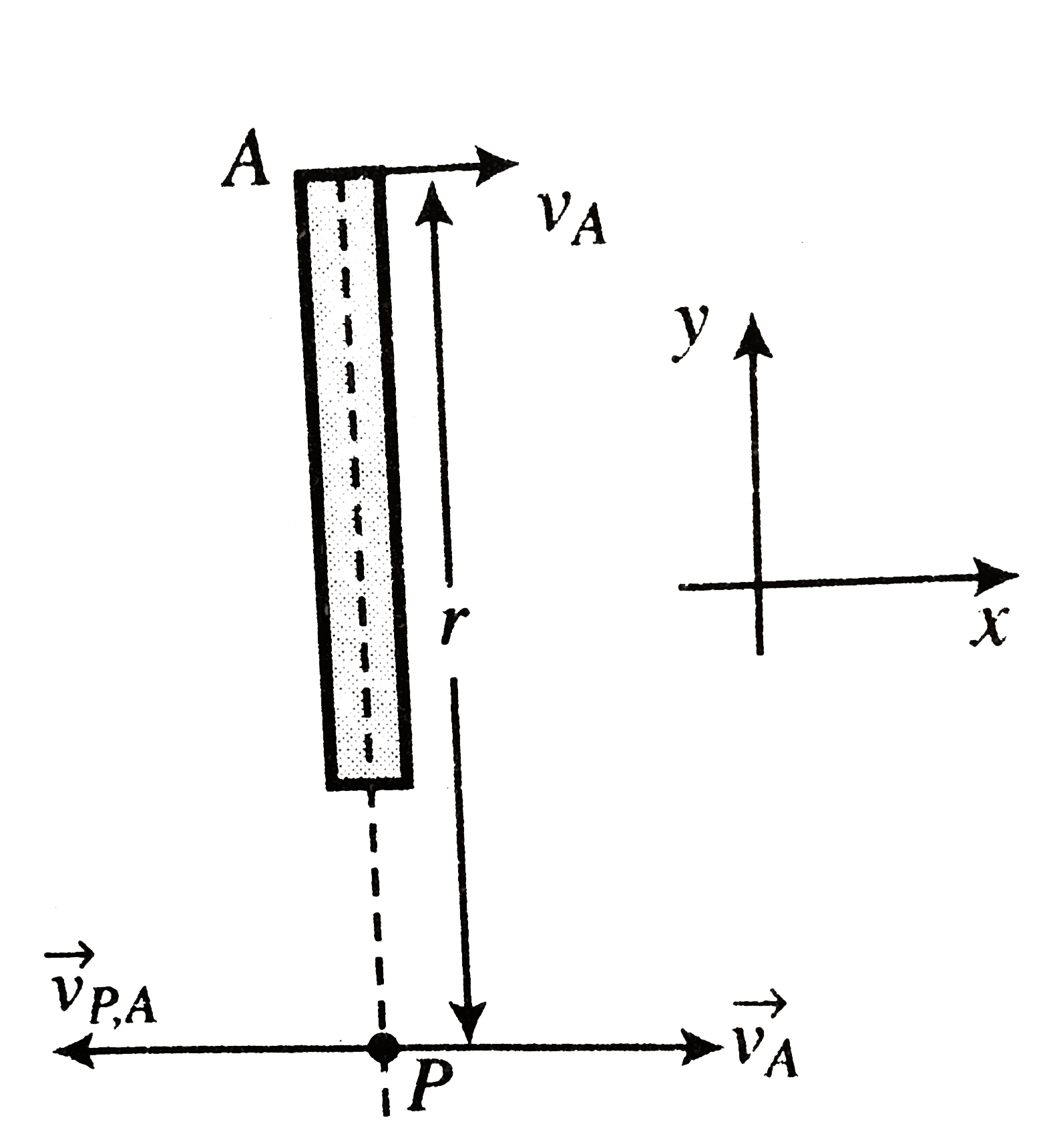Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|9 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.1|6 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1-Integer
- Find the instantneous axis of rotation of a rod length l when its end ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder with r= 0.1 m and mass M = 2 kg is placed such that i...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length 1 m and mass 2 kg is suspended. Calculate tens...
Text Solution
|
- In all the four situations depicted in Column-I, a ball of mass m is c...
Text Solution
|
- A square plate ABCD of mass m and side l is suspended with the help of...
Text Solution
|
- Four spheres A, B, C, D, each of mass m and diameter 2 a are placed wi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder rests on a cart as shown. The coefficient of static...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m, radius R is placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m, radius R is placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m, radius R is placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A light rigid rod of length 4 m is connected rigidly with two identica...
Text Solution
|
- A light rigid rod of length 4 m is connected rigidly with two identica...
Text Solution
|