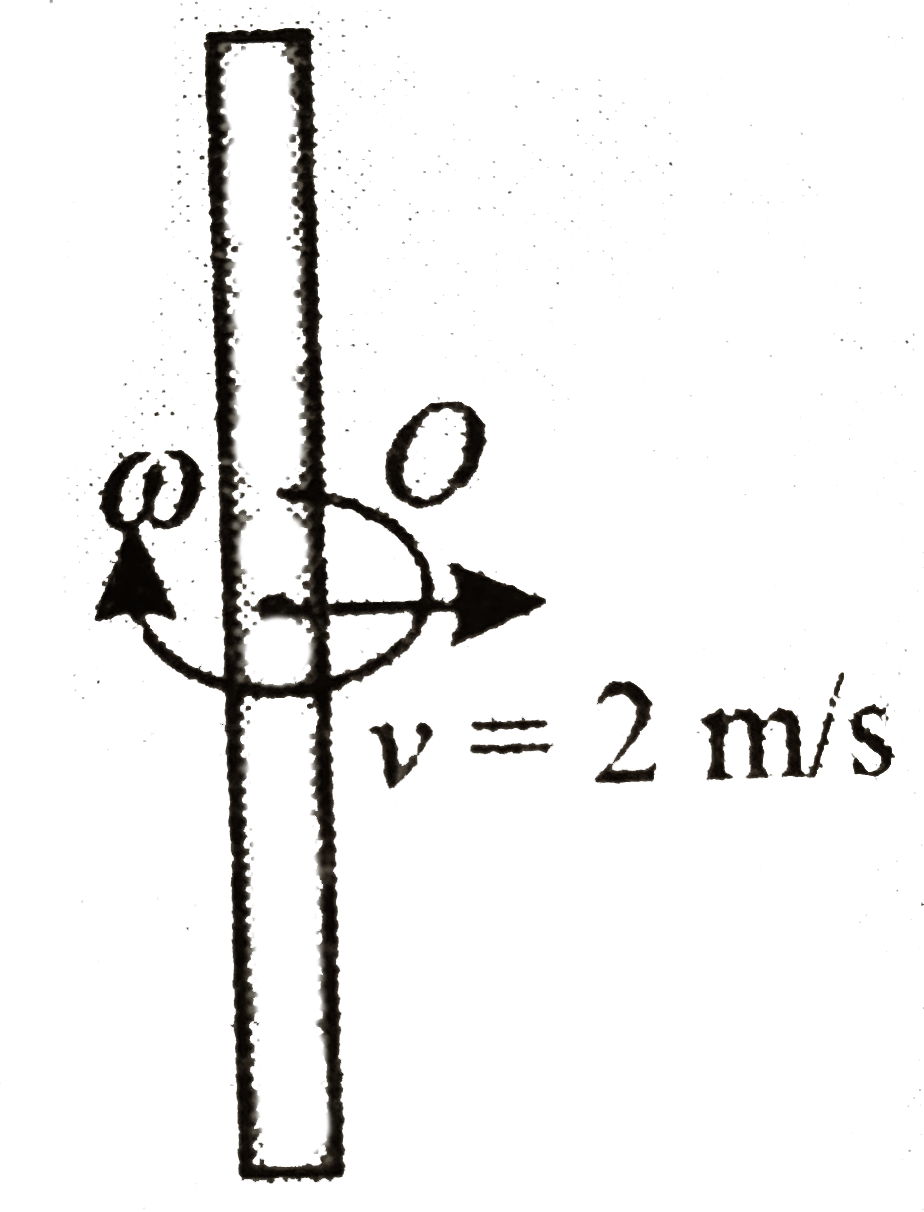Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.2|17 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.3|15 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|9 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1-Exercise 2.1
- The rod of length l=1 m rotates with an angular velocity omega=2 rads^...
Text Solution
|
- The angular velocity and angular acceleration of the pivoted rod are g...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB length 5 m which remains in vertical plane has its ends A and...
Text Solution
|
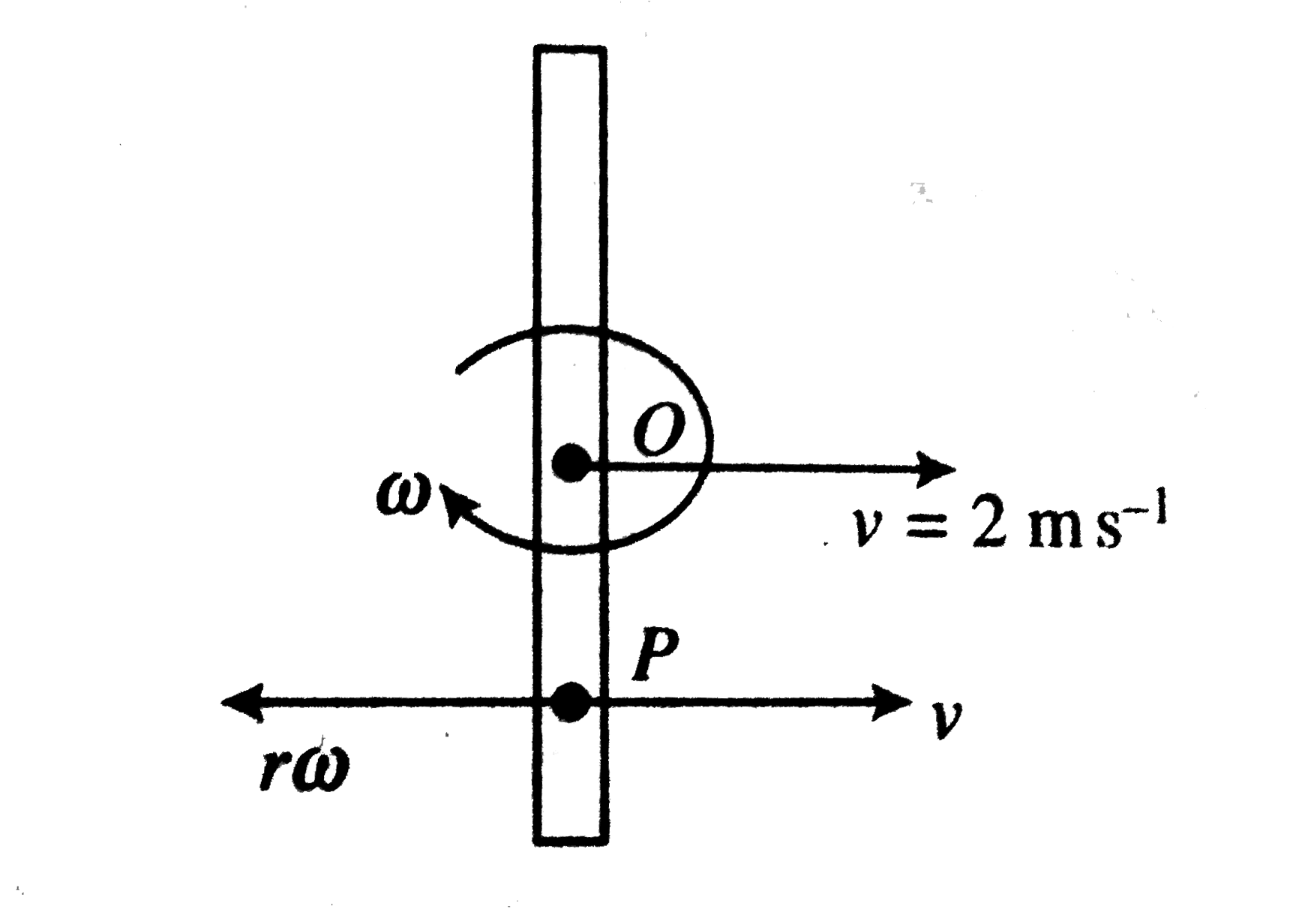
- Shown in the figure is rod which moves with v=2ms^(-1) and rotates wit...
Text Solution
|
- Find the position of instantaneous centre of rotation and angular velo...
Text Solution
|
- A rotating disc moves in the positive direction of the x-axis. Find th...
Text Solution
|