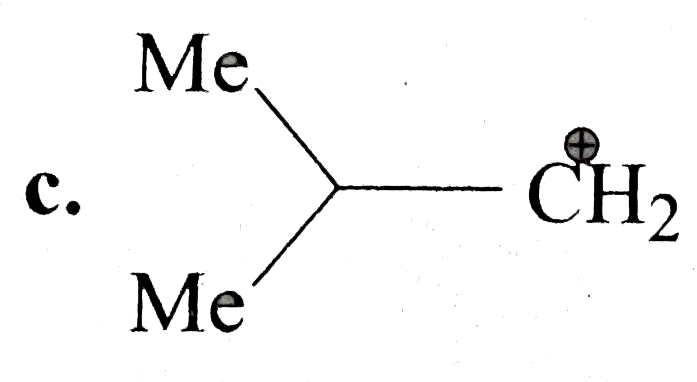
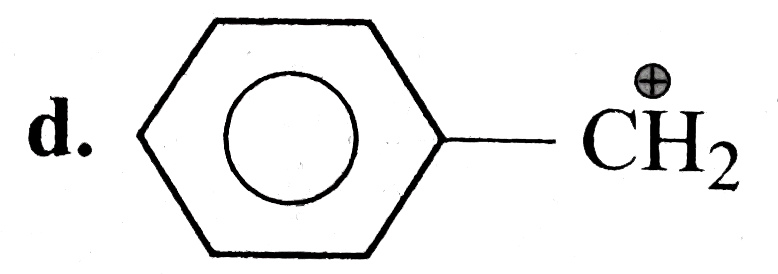
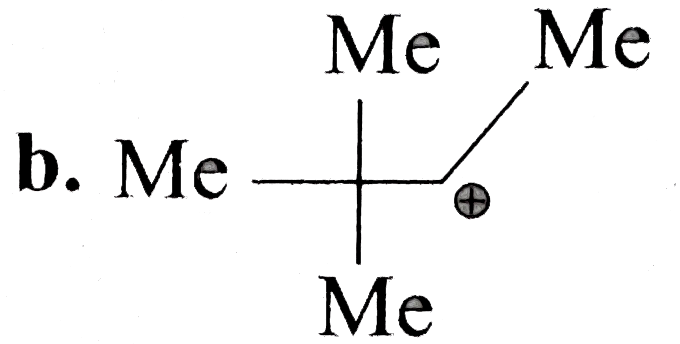A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|23 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|5 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|20 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive Type|3 VideosHYDROGEN, WATER AND HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Archive (Subjective)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Multiple Correct
- Which of the following statement is correct ?
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following Delta G decreases if there can be some intra...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is a hard acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement (s) is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group (s) is/are o- and p-directing ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group (s) is/are m-directing ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are nucleophiles ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are electrophiles ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following have +M effect (overline e - donating mesomer...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following have -M effect (overline e - withdrawing mesome...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement (s) is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statemenet (s) is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement (s) is/are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which benzene sulphonic acid and p-nitrophenol are treated with NaHCO3...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing order of pKa value of the following is : (I)
Text Solution
|
- Among the following which is correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Which one (s) is/are true ?
Text Solution
|