Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercis-2 PART 3|10 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercis-2 PART 4|6 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercis-2 PART 1|14 VideosELECTRODYNAMICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced level problems|31 VideosELECTROSTATICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise HLP|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Exercis-2 PART 2
- A plane spiral with a great number N of turns wound tightly to one ano...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, CDEF is a fixed conducting smooth frame in vertical pla...
Text Solution
|
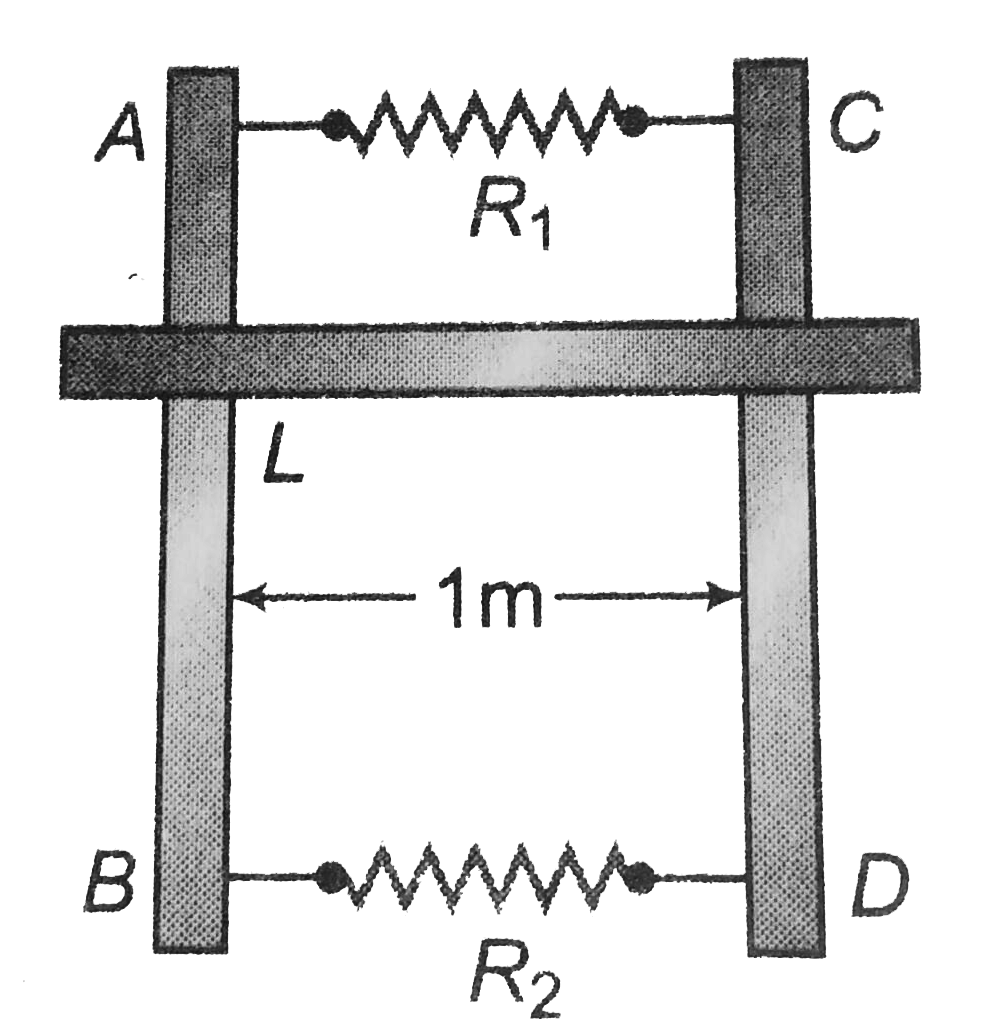
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel long smooth conducting rails separated by a distance l ar...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carries a current I(0), at distance a and b=3a fr...
Text Solution
|
- A square metallic loop of side l is placed near a fixed long wire carr...
Text Solution
|
- A wire loop enclosing a semi-circle of radius a=2cm is located on the ...
Text Solution
|
- A square wire frame ( initially current is zero) with side a and a str...
Text Solution
|
- A II-shaped conductor is located in a uniform magnetic field perpendic...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit diagram shown in the figure the switches S(1) and S(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- A closed circuit consists of a source of constant emf E and a choke co...
Text Solution
|
- A very small circular loop of radius a is initially (at t = 0) coplana...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown two loops ABCD & EFGH are in the same plane.The sm...
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid of length 20cm, area of cross- section 4.0 cm^2 and having ...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in figure is in the steady state with switch S(1) c...
Text Solution
|
- Initially the 900muF capacitor is charged to 100 V and the 100muF capa...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown switches S(1) and S(2) have been closed for 1 sec...
Text Solution
|