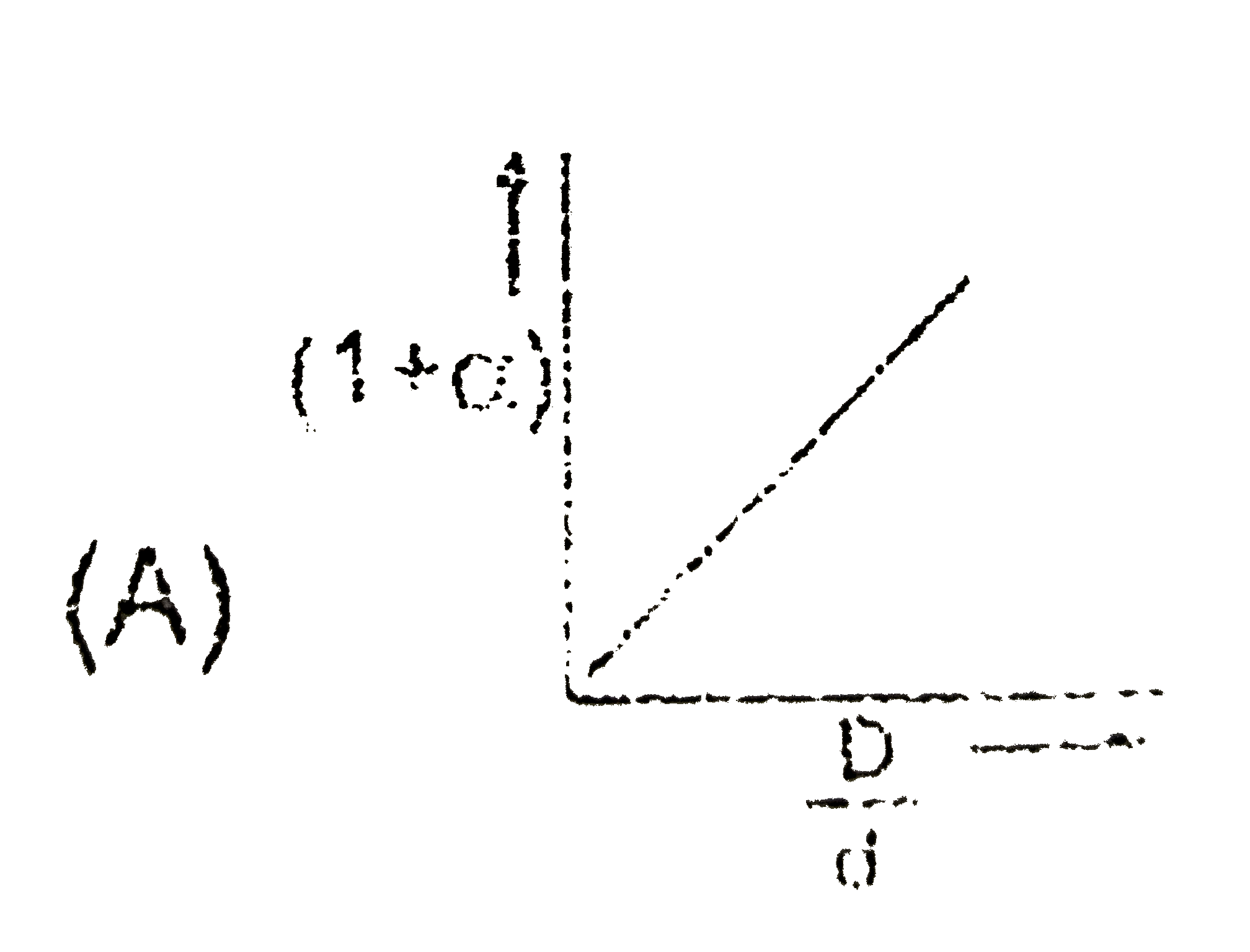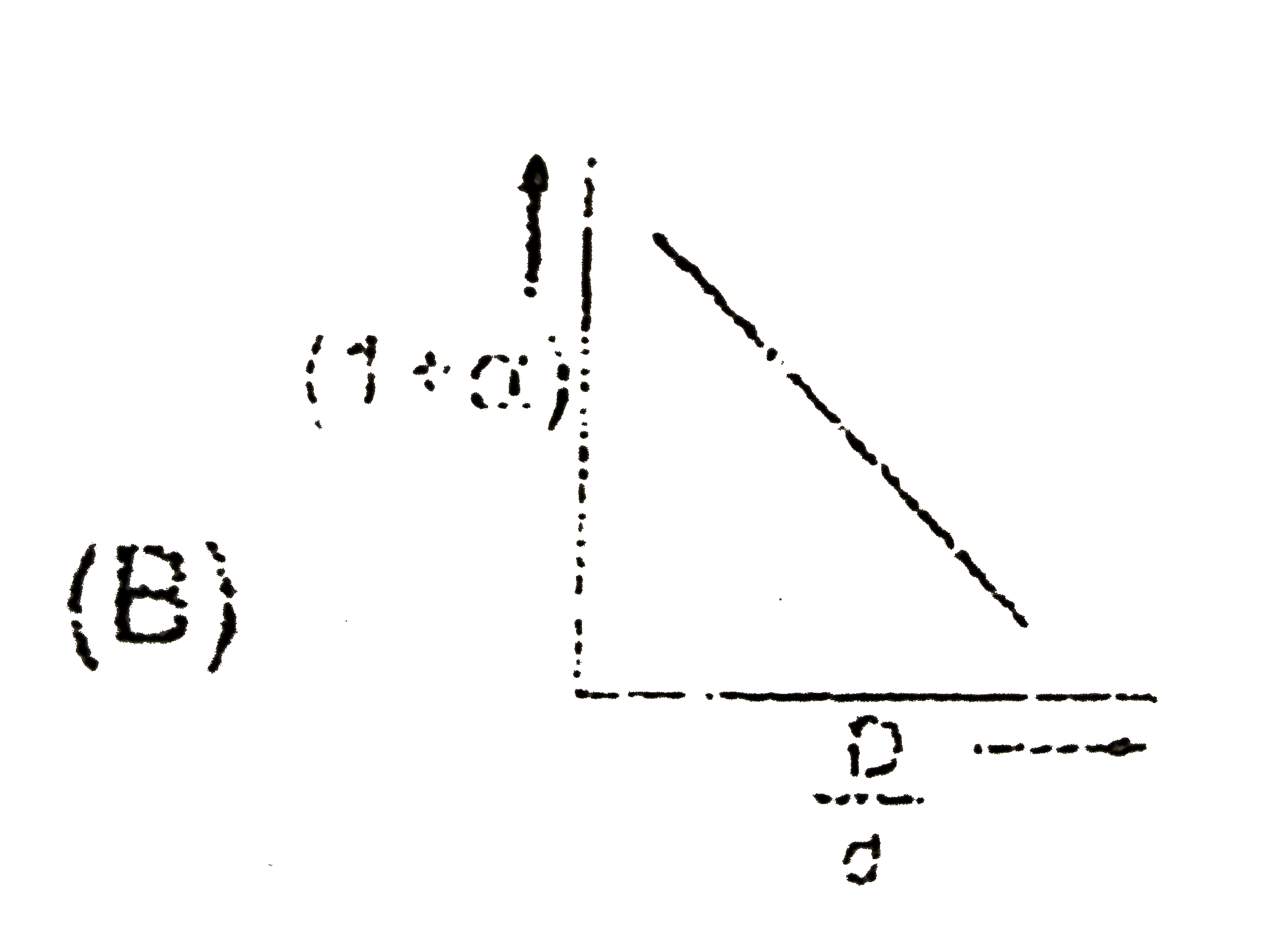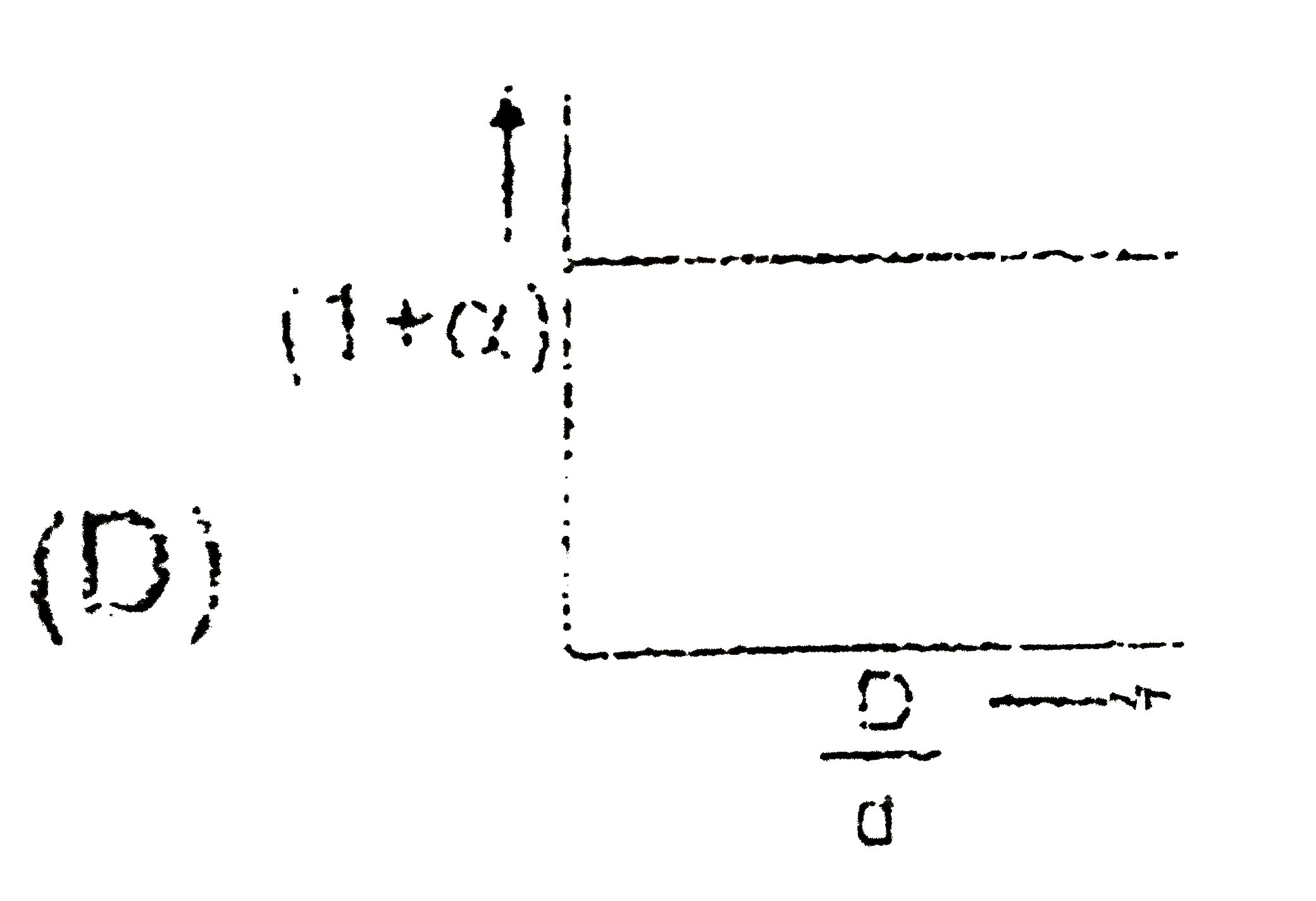A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 (Part-1)|28 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 (Part-2)|22 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1 (Part-1)|38 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Fundamental Concept )|6 VideosD & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Match the column|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Exercise-1 (Part-2)
- For the dissociation reaction N(2)O(4) (g)hArr 2NO(2)(g), the degree o...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation of SO(3) is alpha at equilibrium pressure P...
Text Solution
|
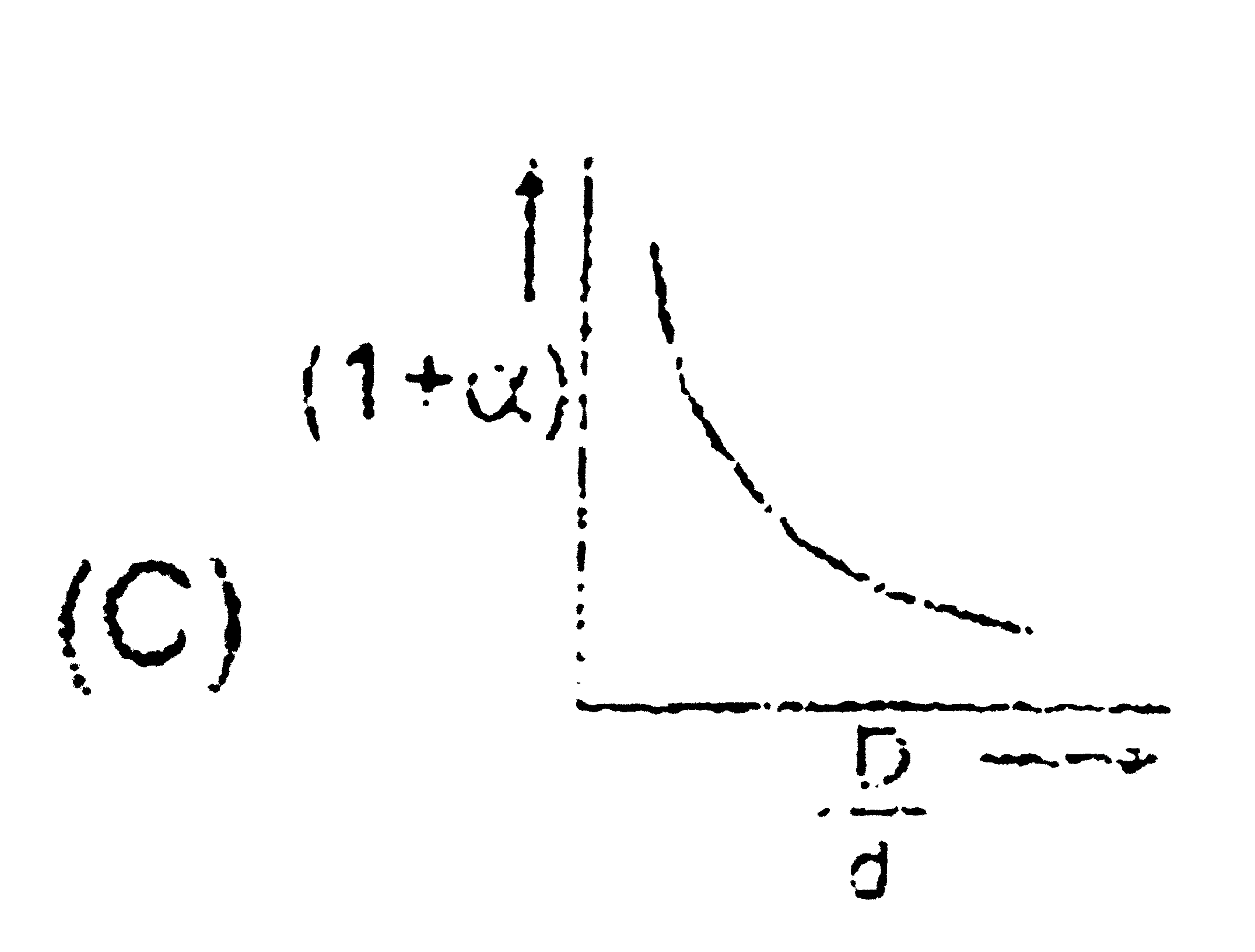
- In the dissociation of N(2)O(4) into NO(2), (1+ alpha) values with the...
Text Solution
|
- N2O4rarr2NO2 In the above equation, alpha varies with (D)/(d) accordin...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction N2O4 hArr 2NO2(g), if percentage dissociation of N2O4...
Text Solution
|
- At a certain temperature T, a compound AB(4)(g) dissociates as 2AB(4...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation of PCl(5)(g) for the equilibrium PCl(5)(g)h...
Text Solution
|
- At 727^(@)C and 1.2 atm of total equilibrium pressure, SO(3) is partia...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following hypothetical equilibrium 2B(g)hArrB(2)(g) I...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour density of fully dissociated NH(4)Cl would be
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation is 0.5 at 800K and 2 atm for the gaseous r...
Text Solution
|
- SO(3)(g)hArrSO(2)(g)+(1)/(2)O(2)(g) If observed vapour density of mi...
Text Solution
|
- What is the minimum mass of CaCO3(s), below which it decomposes comple...
Text Solution
|
- If 50% of CO(2) converts to CO at the following equilibrium: (1)/(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Solid ammonium carbamate dissociate to give ammonia and carbon dioxide...
Text Solution
|
- For NH(4)HS(s)hArrNH(3)(g)+H(2)S(g) reaction started only with NH(4)HS...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the decomposition of solid NH(4)HS in a flask containing NH(3...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relative humidity of air at 1 bar pressure and 313K temper...
Text Solution
|
- For the equilibrium CuSO(4)xx5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4)xx3H(2)O(s) + 2H(2)O(...
Text Solution
|
- (a) CuSO(4).5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4).3H(2)O(s)+2H(2)O(g) K(p)=4xx10^(-4)at...
Text Solution
|