A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 (Part-1)|28 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 (Part-2)|22 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1 (Part-1)|38 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Fundamental Concept )|6 VideosD & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Match the column|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Exercise-1 (Part-2)
- For NH(4)HS(s)hArrNH(3)(g)+H(2)S(g) reaction started only with NH(4)HS...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the decomposition of solid NH(4)HS in a flask containing NH(3...
Text Solution
|
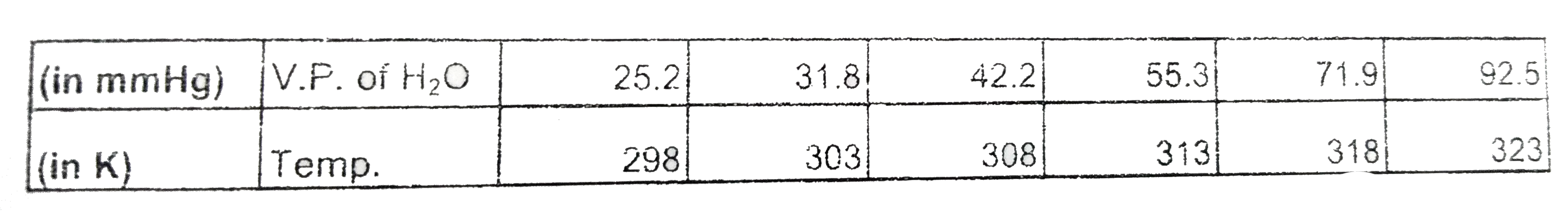
- What is the relative humidity of air at 1 bar pressure and 313K temper...
Text Solution
|
- For the equilibrium CuSO(4)xx5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4)xx3H(2)O(s) + 2H(2)O(...
Text Solution
|
- (a) CuSO(4).5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4).3H(2)O(s)+2H(2)O(g) K(p)=4xx10^(-4)at...
Text Solution
|
- For the equilibrium CuSO(2).5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4).3H(2)O(s)+2H(2)O(g) ...
Text Solution
|
- CuSO(4).5H(2)O(s)hArrCuSO(4). 3H(2)O(s)+2H(2)O(g), K(p)=4xx10^(-4)atm^...
Text Solution
|
- The correct relationship between free energy change in a reaction and ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, H(2)(g)+I(2)(g)hArr 2HI(g), K(c)^(@)=66.9 at 350^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constants for the reaction Br(2)hArr 2Br at 500 K an...
Text Solution
|
- An exothermic reaction is represented by the graph :
Text Solution
|
- An endothermic reaction is represented by the graph:
Text Solution
|
- The value of DeltaG^(@) for a reaction in aqueous phase having K(c)=1,...
Text Solution
|
- The effect of temperature on equilibrium constant is expressed as(T(2)...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction CO(g)+H(2)O(g) hArr CO(2)(g)+H(2)(g) at a given t...
Text Solution
|
- Given the following reaction at equilibrium N(2)(g) + 3H(2)(g)hArr2NH(...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium SO(2)Cl(2)(g) hArr SO(2)(g)+Cl(2)(g) is attained at 25...
Text Solution
|
- Densities of diamond and graphite are (3.5g)/(mL) and (2.3g)/(mL). C...
Text Solution
|
- Introduction of inert gas (at the same temperature) will affect the eq...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium SO(2)Cl(2)(g) hArr SO(2)(g)+Cl(2)(g) is attained at 25...
Text Solution
|