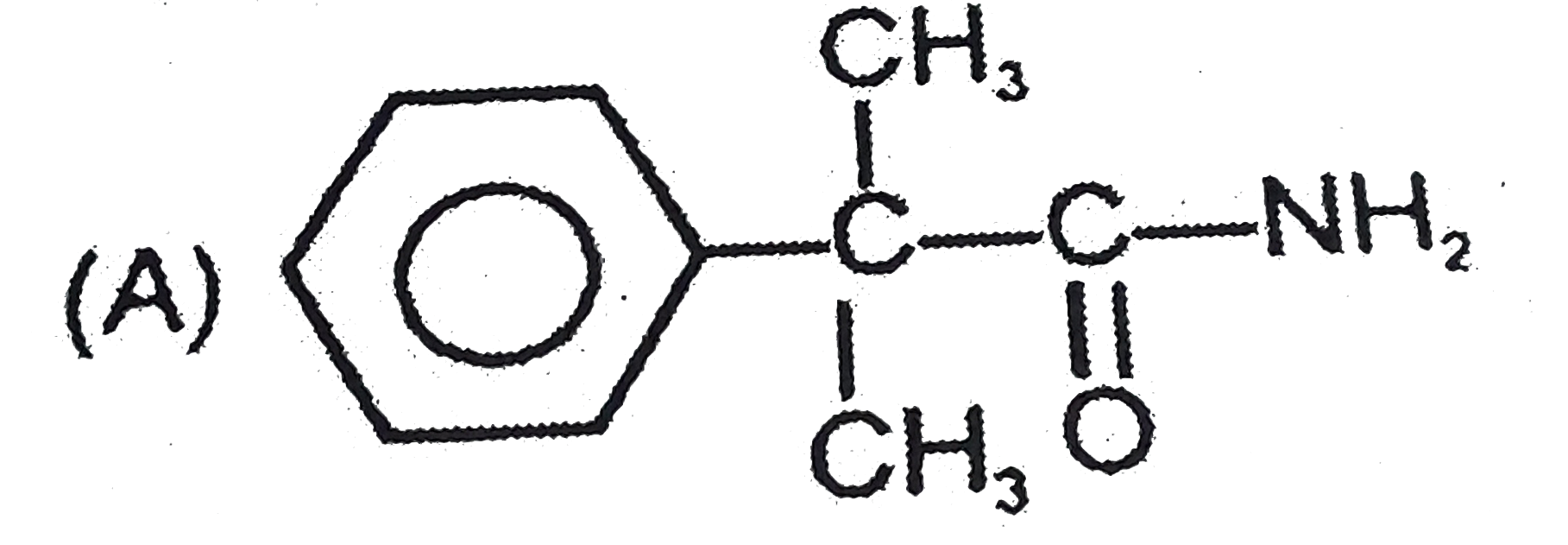
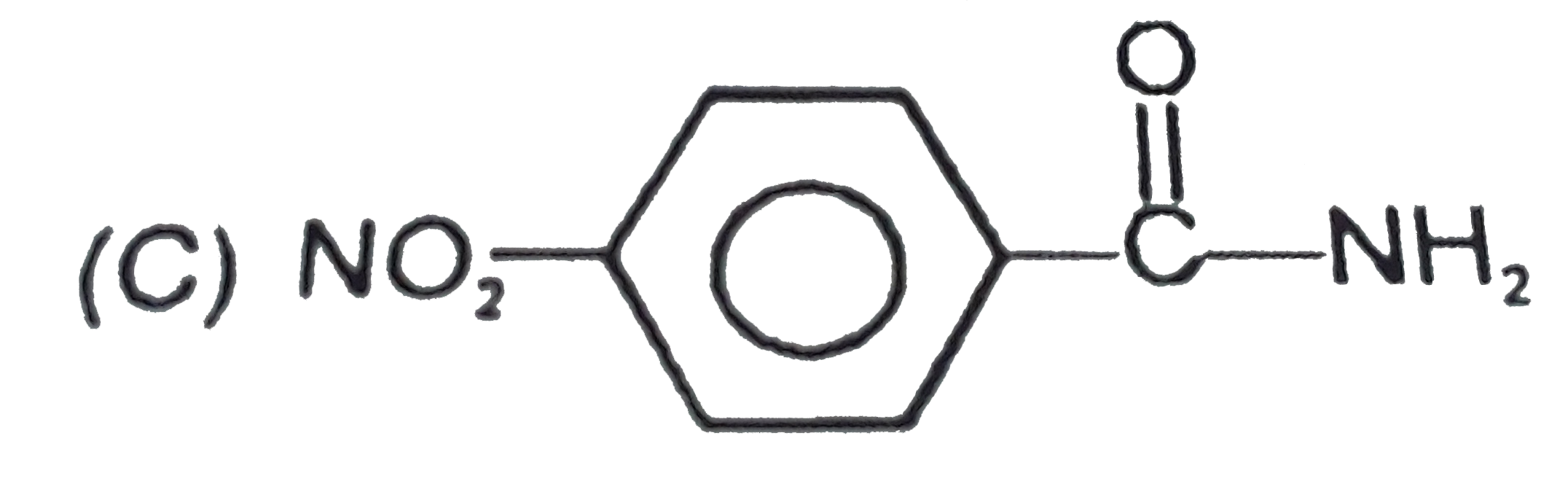
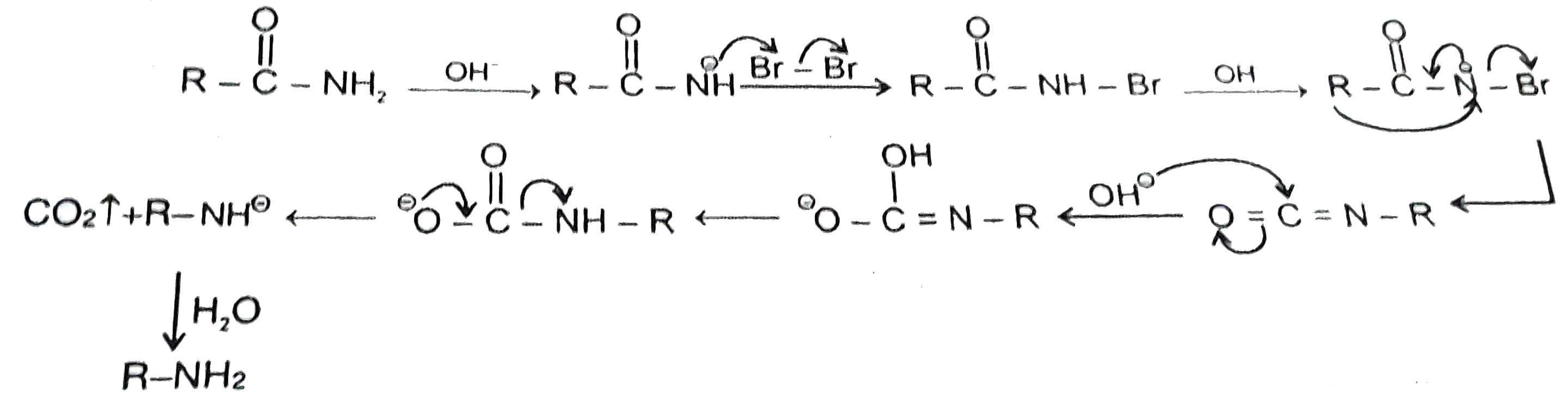A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise -3 Part-I|36 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-II JEE MAIN|19 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-III ONE OR MORE THAN ONE OPTION CORRECT TYPE|10 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Fundamental Concept )|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS -PART IV- COMPREHENSION
- Which of the following compound is 'P' ?
Text Solution
|
- S is a well known pain killer which of the following is 'R'?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is attacking spcies in conversion Y to P?
Text Solution
|
- The intermediates which are involved in the conversion from benzamide ...
Text Solution
|
- (B) on treatment with Zn//HCl gives :
Text Solution
|
- (D) on reaction with phenol under alkaline conditions gives :
Text Solution
|
- The -NO(2) group in an aromatic ring deactivates the ortho and para po...
Text Solution
|
- The -NO(2) group in an aromatic ring deactivates the ortho and para po...
Text Solution
|
- The -NO(2) group in an aromatic ring deactivates the ortho and para po...
Text Solution
|
- Hofmann rearrangement In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstitued a...
Text Solution
|
- Hofmann rearrangement In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstitued a...
Text Solution
|
- Answer questions 1, 2 and 3 by appropriately matching the information ...
Text Solution
|
- Q.12, Q.13 and Q.14 by appropriately matching the information given in...
Text Solution
|