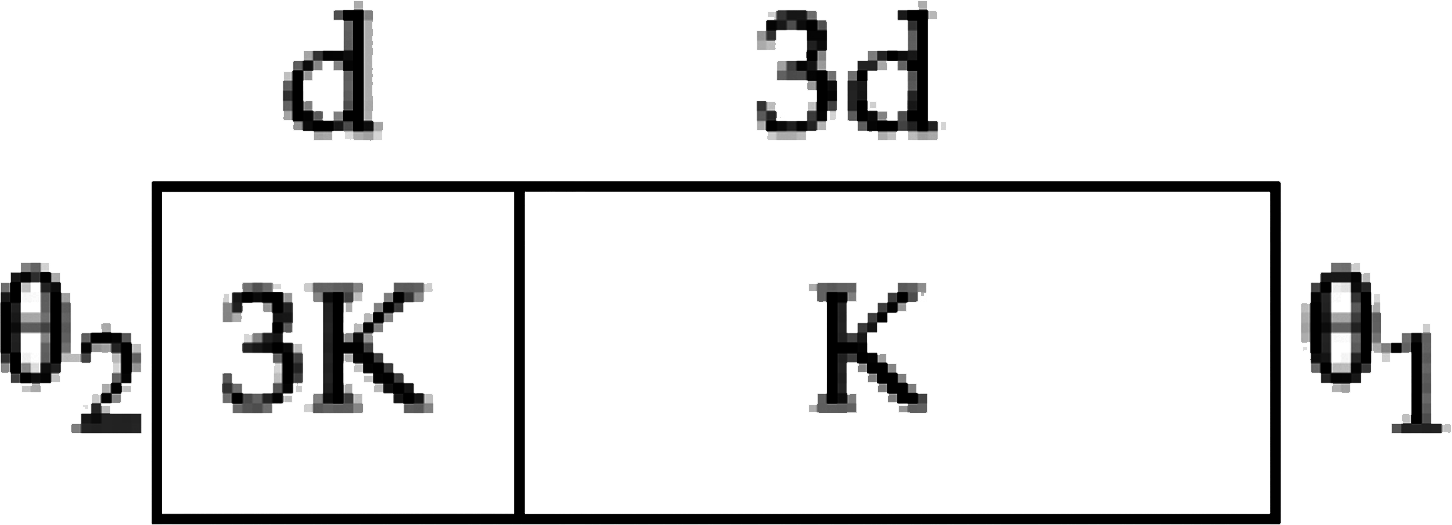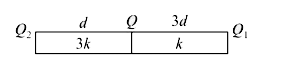A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST 11 (2020) -PHYSICS (SECTION - 2)
- Two materials having coefficients of thermal conductivity '3k' and 'k'...
Text Solution
|
- The position vector of a particle changes with time according to the d...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance =3Omega and length l is stretched to doub...
Text Solution
|
- Moment of inertia of a body about a given axis is 1.5 kg m^(2). Initi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens L (refractive index =1.5) is placed on a plane mirr...
Text Solution
|
- Two coils 'P' and 'Q' are separated by some distance. When a current o...
Text Solution
|