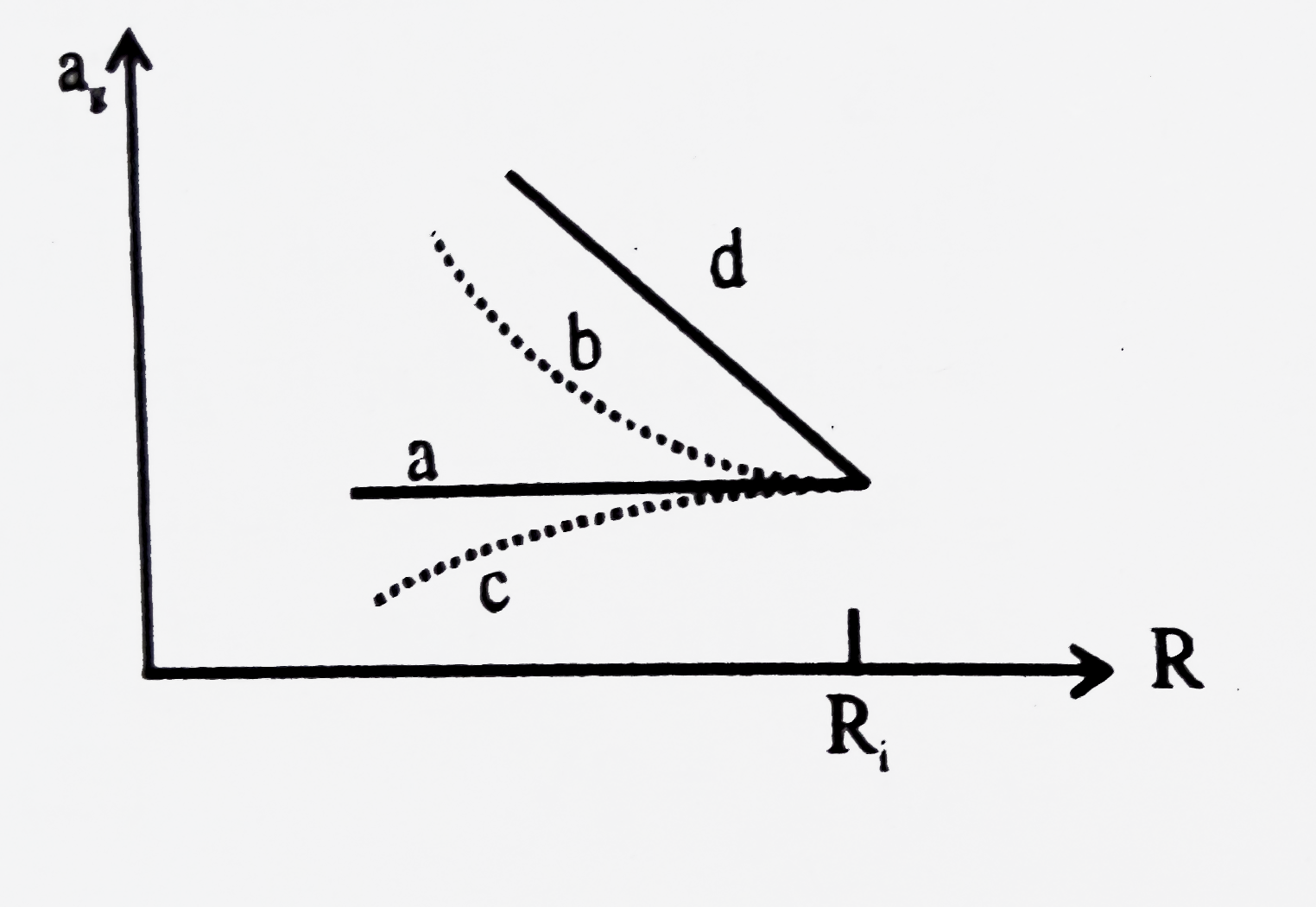
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Main (Archive)|43 VideosGRAVITATION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance (Archive) SINGLE OPTION CORRECT|14 VideosGRAVITATION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-1 MCQs|60 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (ARCHIVE )|111 VideosINTRODUCTION TO VECTORS & FORCES
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced ( ARCHIVE LEVEL-2)|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-GRAVITATION-Level-2
- Gravitational force with which a body attracts the other is always equ...
Text Solution
|
- A body starts from rest from a point distant r(0) from the centre of t...
Text Solution
|
- A(nonrotating) star collaps onto from an initial radius R(i) with its ...
Text Solution
|
- If ge, gh and gd be the acceleration due to gravity at earth’s surfac...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration due to gravity on the planet A is 9 times the acceler...
Text Solution
|
- If the earth were to spin faster, acceleration due to gravity at the p...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the earth to be a sphere of uniform density the acceleration ...
Text Solution
|
- Three planets of same density have radii R(1),R(2) and R(3) such that ...
Text Solution
|
- Two objectes of mass m and 4m are at rest at and infinite seperation. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two uniform spherical stars made of same material have radii R and 2R....
Text Solution
|
- Two uniform spherical starts made of same material have radii R and 2...
Text Solution
|
- A body weighs 64 N on the surface of the Earth. What is the gravitatio...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is launched into a circular orbit of radius 'R' around ear...
Text Solution
|
- A planet of small mass m moves around the sun of mass M along an ellip...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the variation of energy with the orbit radius of a bo...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite revolves in the geostationary orbit but in a direction eas...
Text Solution
|
- A satallite of mass m, initally at rest on the earth, is launched into...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass 5M orbits the earth in a circular orbit. At one po...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth in an orbit o...
Text Solution
|
- When a satellite in a circular orbit around the earth enters the atmos...
Text Solution
|