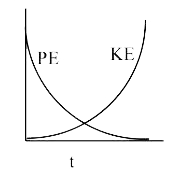
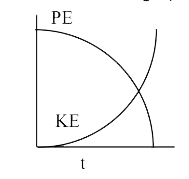
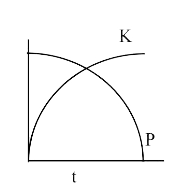
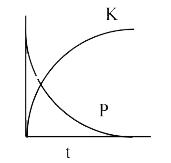
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level - 1 PARAGRAPH QUESTIONS|3 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2|48 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 0 - LONG ANSWER TYPE|5 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (ARCHIVE )|111 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ENERGY & MOMENTUM-Level - 1
- For a block of mass m to slide without friction up the rise of height ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular block is mobing along a frictionless path, when it encou...
Text Solution
|
- A particle falls from rest under gravity. Its potential energy with re...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is released from height h on smooth quarter circu...
Text Solution
|
- A block is released from the top of two inclined rough surfaces of hei...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is given an initial speed u inside a smooth spherical shell...
Text Solution
|
- A small object of mass m, on the end of a light cord, is held horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is rotated in vertical circle by connecting it to string f...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle of weight w, attached to a fixed point by a light ine...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs A and B(kA=2kB) are stretched by applying forces of equal ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is initially moving to the right on a horizontal fri...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal 50 N force acts on a 2 kg crate which is at rest on a smo...
Text Solution
|
- The speed v reached by a car of mass m in travelling a distance x, dri...
Text Solution
|
- The first graph shows the potential energy U(x) for a particle moving...
Text Solution
|
- Potential energy of a particle is related to x coordinate by equation ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 15 kg has an initial velocity vecv(i) = hati - 2 ha...
Text Solution
|
- A U-shaped wire has a semicircular bending between A and B as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Two carts (A and B), having spring bumpers, collide as shown. Cart A h...
Text Solution
|
- An open water tight railway wagon of mass 5xx10^(3) kg coasts at initi...
Text Solution
|
- A 64-kg woman stands on frictionless ice. She kicks a 0.10-kg stone ba...
Text Solution
|