Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
VERY SIMILAR TEST 4
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) (GROUP A)|10 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 4
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) (GROUP B)|9 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 4
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION A (BOTANY) (GROUP B)|9 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 2
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - B (Zoology)|26 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 5
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) GROUP C|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN-VERY SIMILAR TEST 4-SECTION A (BOTANY) (GROUP C)
- Answer any two of the following : 5. Explain Griffith.s experiment, ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer any two of the following : (i) Explain the role of DNA depend...
Text Solution
|
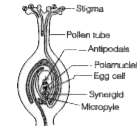
- Answer any two of the following : (i) Draw a longitudinal section of...
Text Solution
|
- Answer any two of the following : Explain the process of sewage wate...
Text Solution
|