Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE - 05 (B)
- The ends Q and R of two thin wires, PQ and RS, are soldered (joined) t...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a movable frictionless piston. It...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal mono-atomic gas is taken round cyclic process ABC...
Text Solution
|
- A solid body X of heat capacity C is kept in an atmosphere whose tempe...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas, initially at pressure p1 and vol...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken through a cycle ABCA as ...
Text Solution
|
- An ice cube of mass 0.1 kg at 0^@C is placed in an isolated container ...
Text Solution
|
- A monoatomic ideal gas of two moles is taken through a cyclic process ...
Text Solution
|
- A 5 m long cylindrical steel wire with radius 2xx10 ^(-3) m is sus...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical box of side 1 m contains helium gas (atomic weight 4) at a p...
Text Solution
|
- An insulated box containing a monoatomic gas of molar mass (M) moving ...
Text Solution
|
- The top of an insulated cylindrical container is covered by a disc hav...
Text Solution
|
- The piston cylinder arrangement shown contains a diatomic gas at tempe...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of coefficient of linear expansion alpha(s) is floating in a b...
Text Solution
|
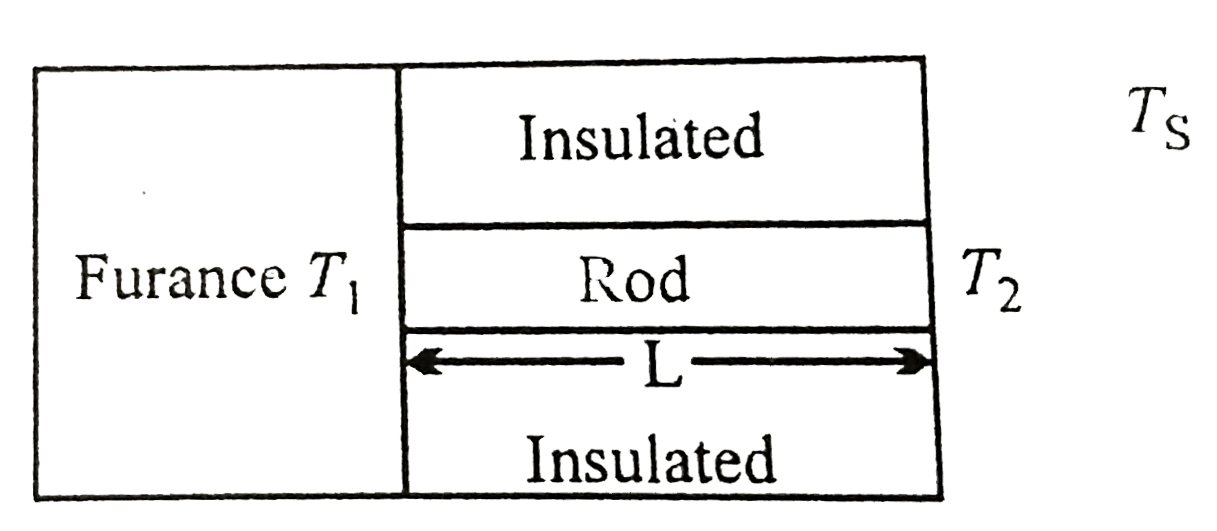
- One end of rod of length L and cross-sectional area A is kept in a fur...
Text Solution
|
- A metal of mass 1 kg at constant atmospheric pressure and at initial t...
Text Solution
|
- In a insulated vessel, 0.05 kg steam at 373 K and 0.45 kg of ice at 25...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod AB of length 10 x has its one end A in ice at 0^(@)C and t...
Text Solution
|
- A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state i with internal ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal is heated in a furnace where a sensor is kept above the metal ...
Text Solution
|