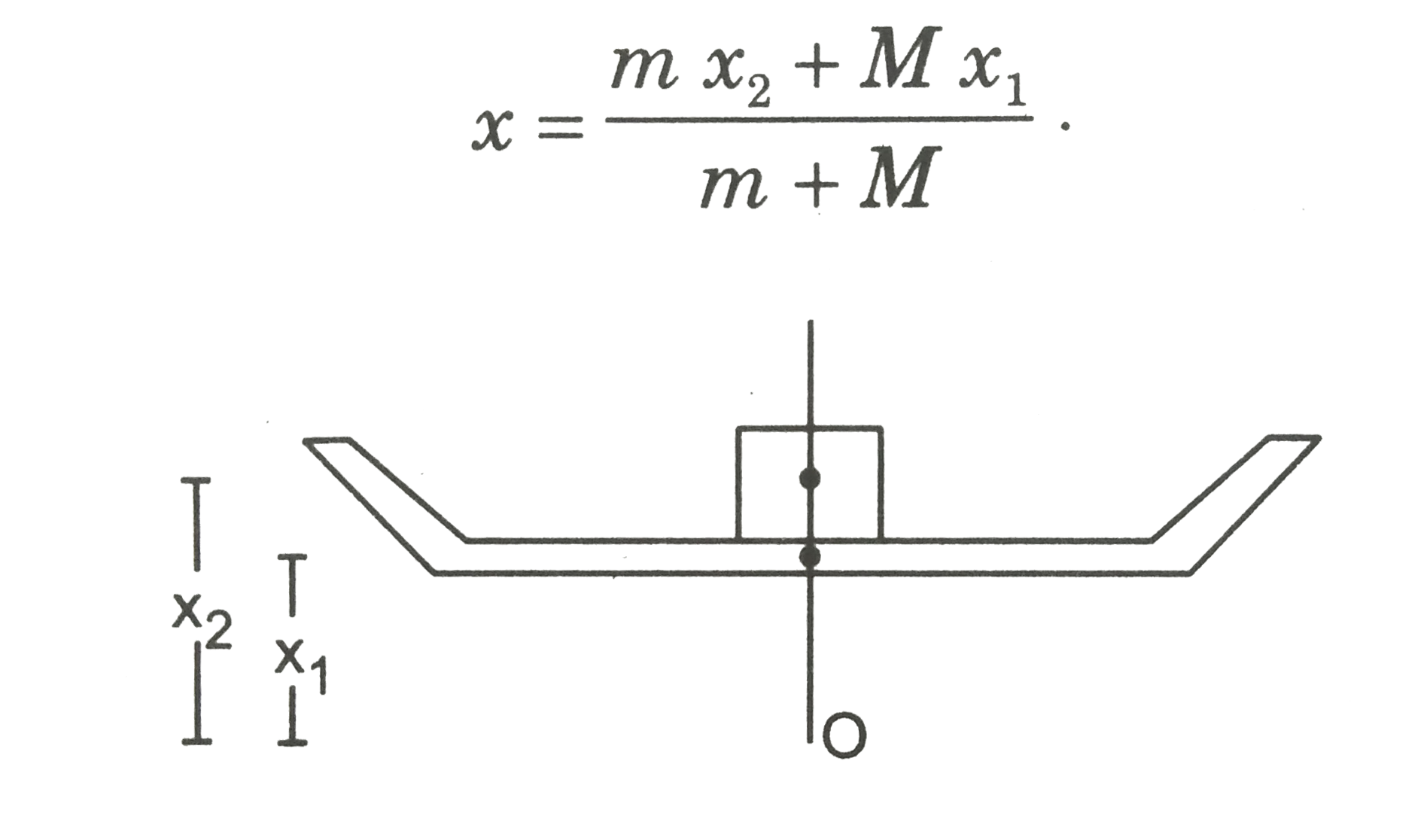Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM, COLLISION
HC VERMA|Exercise Question For short Answer|25 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM, COLLISION
HC VERMA|Exercise Objective -1|18 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM, COLLISION
HC VERMA|Exercise Exercises|64 VideosCALORIMETRY
HC VERMA|Exercise Exercises|18 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
HC VERMA|Exercise Exercises|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM, COLLISION-worked out Examples
- Half of the recrtangular plate shown in figure is made of a material o...
Text Solution
|
- The density of a rod of length L varies as rho=A+Bx where x is the dis...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L is placed in a large tray ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a system of two identical particles having mass m. If one of ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2.5 kg is subjected to the forces shown in figure. Find...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of equal mass m are connected by an unstreched spring and p...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of equal mass m are connected by an unstretched spring and ...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile is fired at a speed of 100 m/s at an angel of 37^0 above ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is placed on the top of a bigger block of mass 10 M ...
Text Solution
|
- The hero of a stunt film fires 50 g bullets from a machine gun, each a...
Text Solution
|
- A block moving horizontally on a smooth surface with a speed of 20 m/s...
Text Solution
|
- A car of mass M is moving with a uniform velocity upsilon on a horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A space shuttle while travelling at a speed of 4000 km/h with respect ...
Text Solution
|
- A boy of mass 25 kg stands on a board of mass 10 kg which in turn is k...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m is standing on a platform of mass M kept on smooth ice...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with a velocity v along X-axis, strikes anothe...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass 50g if fired from below into the bob of mass 450g of ...
Text Solution
|
- A light spring of spring constant k is kept compressed between two blo...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connect to another block of mass M by a massless ...
Text Solution
|
- The two balls shown in figure are identical the first ball is moving a...
Text Solution
|