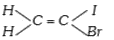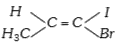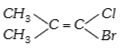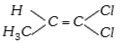A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise PAST YEARS QUESTIONS |85 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|14 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Organic Reactions and their Mechanism )|46 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|7 VideosHYDROCARBONS
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Structural and Stereo Isomerism )
- Compound has the following prefix
Text Solution
|
- No. of geometrical isomers possible for the compound CH(3)-CH=CH-CH=CH...
Text Solution
|
- Which shows geometrical isomerism
Text Solution
|
- Which pair show cis-trans isomerism
Text Solution
|
- Reason for geometrical isomerism shown by 2- butene is
Text Solution
|
- The most stable geometrical isomer among the following is
Text Solution
|
- Separating of d and l enantiorphs from a racemic mixture is called
Text Solution
|
- Number of optical isomers of lactic acid are
Text Solution
|
- Meso-tartaric acid is optically inactive due to the presence of
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds is not chiral
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds is an optically active compound
Text Solution
|
- d-tartaric acid and l-tartric acid are
Text Solution
|
- Stereoisomers which are not mirror image of each other, are called.:
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following organic compound overset(1)CH(3)overset(2)CH(...
Text Solution
|
- If the light waves pass through a nicol prism then all the oscillation...
Text Solution
|
- Disymmetrical object is one which image
Text Solution
|
- What is the possibel number of optical isomer for a compound containin...
Text Solution
|
- A compound whose molecule is superimposabel on its mirror image despit...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds is expected to be optically active ?
Text Solution
|
- Which will show optical isomerism
Text Solution
|