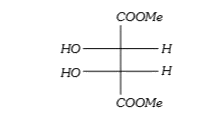
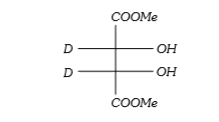
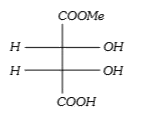
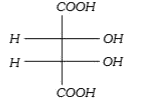
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise PAST YEARS QUESTIONS |85 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|14 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Organic Reactions and their Mechanism )|46 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|7 VideosHYDROCARBONS
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Structural and Stereo Isomerism )
- Which of the following compounds is expected to be optically active ?
Text Solution
|
- Which will show optical isomerism
Text Solution
|
- The optically active molecule is
Text Solution
|
- Which among the following functional groups has been given the hig...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is optically active
Text Solution
|
- The configuration of the chiral centre and the geometry of the double ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following is a correct statement
Text Solution
|
- Products of the reaction
Text Solution
|
- Which compound is optically active
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is not true about enantiomers
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement about the compounds A and B is
Text Solution
|
- Which will give chiral molecule ?
Text Solution
|
- The number of optical isomers of CH3CH(OH)CH(OH)CHO is :-
Text Solution
|
- Consider the structures given below They are
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compound is capcabel of existing in a meso ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following representation They are
Text Solution
|
- The number of chiral centres in D-(+)-glucose is
Text Solution
|
- The number of racemic mixture obtained by optical isomers of 2, 3-dihy...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will exhibit optical isomerism ?
Text Solution
|
- The R– isomers among the following are
Text Solution
|