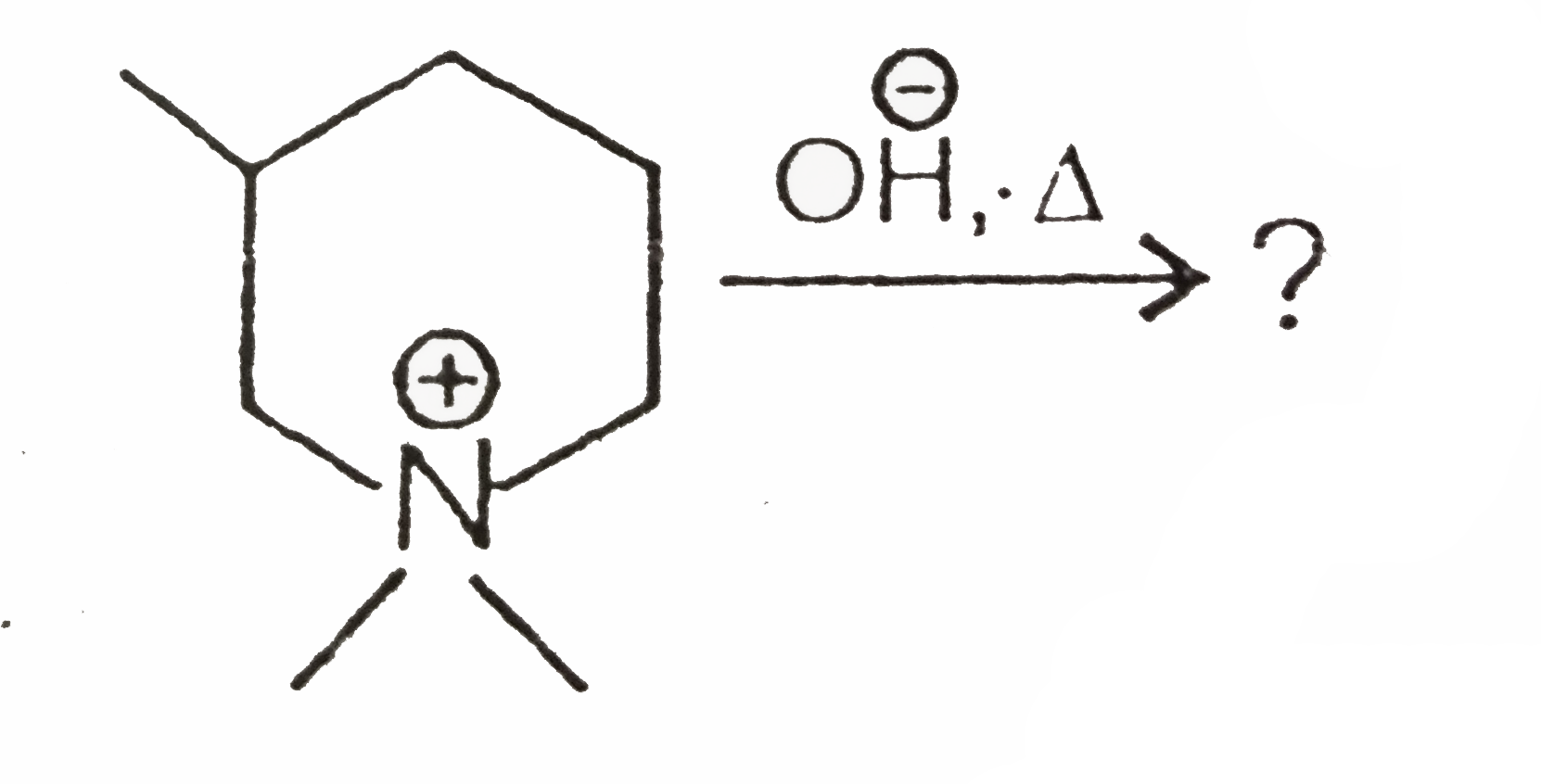
A
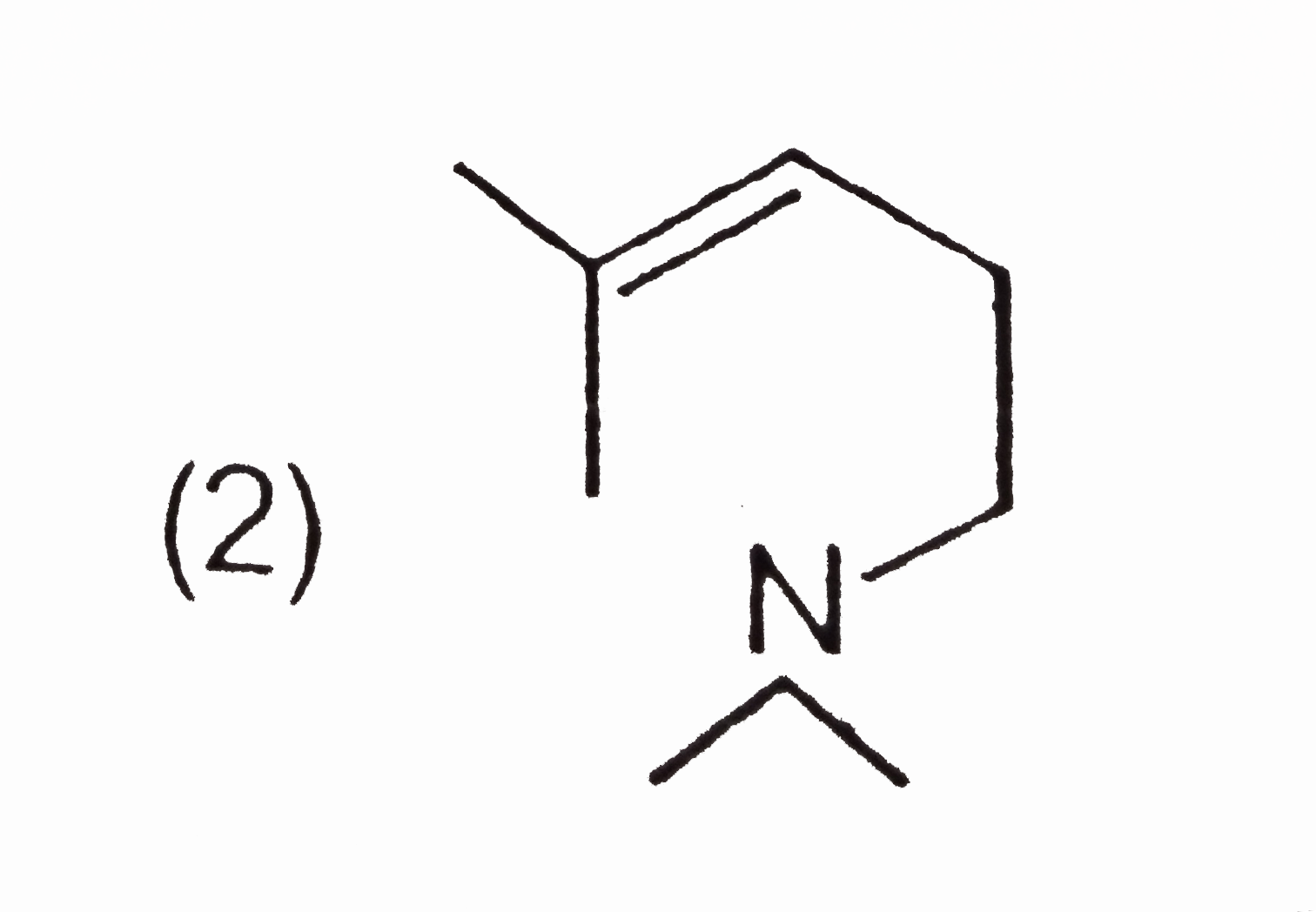
B
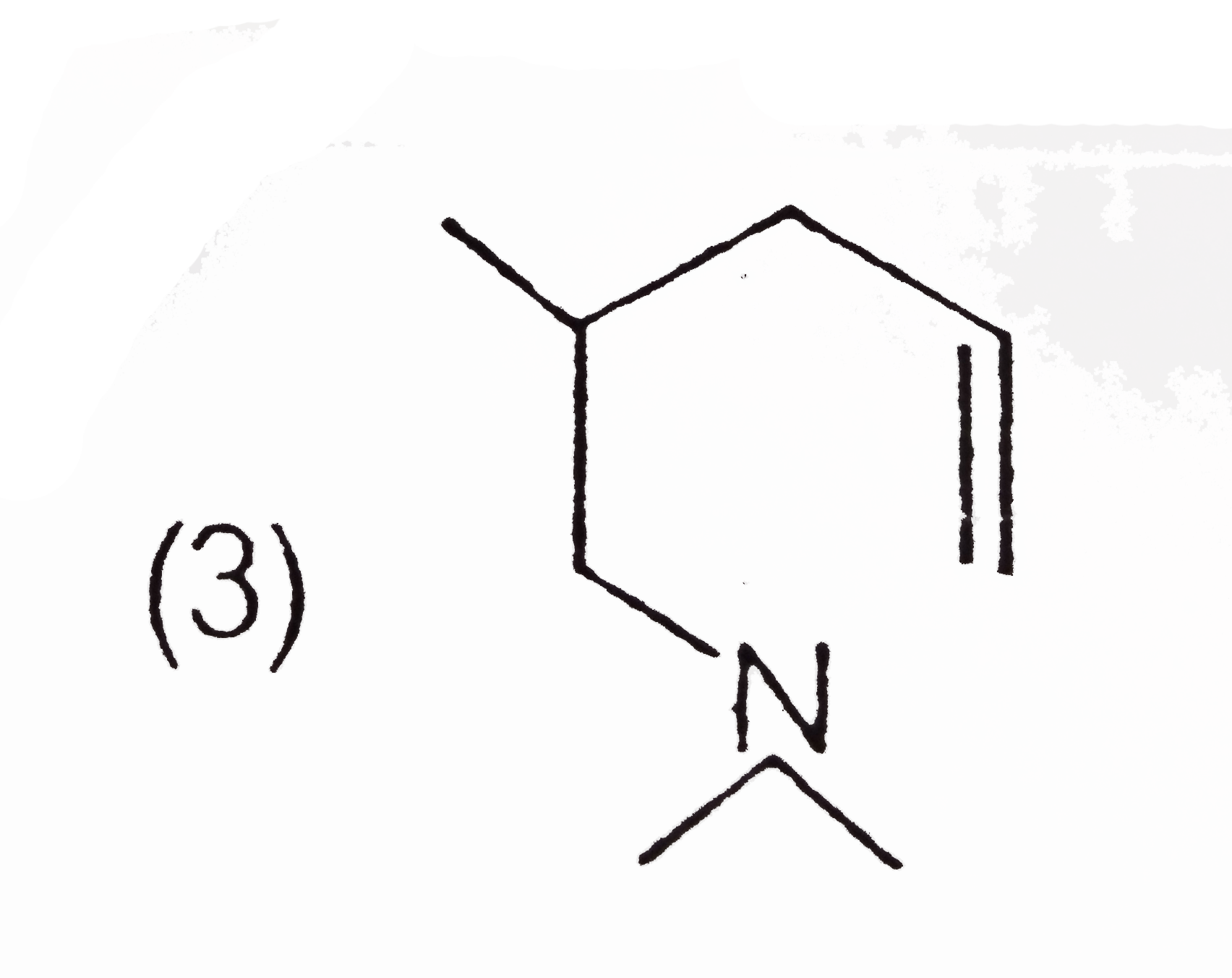
C
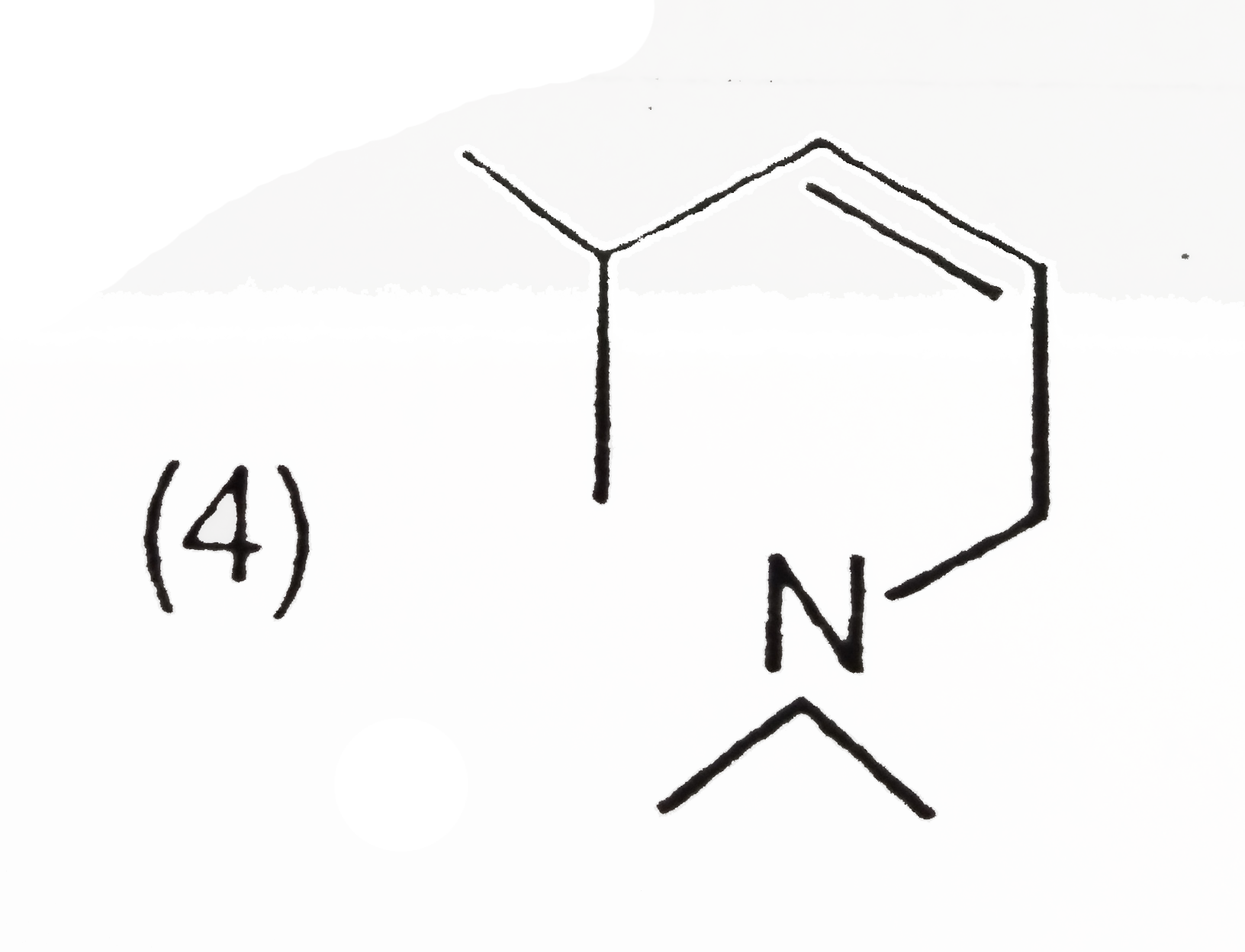
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AMINES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section E Assertion-Reason Type Questions|9 VideosAMINES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section F Matrix- Match Type Questions|1 VideosAMINES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section C (Objective type questions more than one options are correct)|13 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Try Yourself|20 VideosBIOMOLECULES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise EXERCISE (ASSIGNMENT) SECTION - D Assertion - Reason Type Questions|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-AMINES -Assignment Section D Linked Comprehension Type Questions
- Treatment of primary amines with nitrous acid gives diazonium ions. Al...
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of primary amines with nitrous acid gives diazonium ions. Al...
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of primary amines with nitrous acid gives diazonium ions. Al...
Text Solution
|
- The molecular formula of a compound (A) is C(3)H(7)NO. The Compound (A...
Text Solution
|
- The molecular formula of a compound (A) is C(3)H(7)NO. The Compound (A...
Text Solution
|
- The molecular formula of a compound (A) is C(3)H(7)NO. The Compound (A...
Text Solution
|
- Amines are basic in nature and show many types of reactions such as su...
Text Solution
|
- Amines are basic in nature and show many types of reactions such as su...
Text Solution
|
- Amines are basic in nature and show many types of reactions such as su...
Text Solution
|
- Arenediazonium ion are weak electrophiles, they react with highly reac...
Text Solution
|
- Arenediazonium ion are weak electrophiles, they react with highly reac...
Text Solution
|
- Hoffmann-Bromamide reaction has the following mechanism Reagent ...
Text Solution
|
- Hoffmann-Bromamide reaction has the following mechanism The rate...
Text Solution
|
- Hoffmann-Bromamide reaction has the following mechanism The carb...
Text Solution
|