Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-Assignment (SECTION - D)
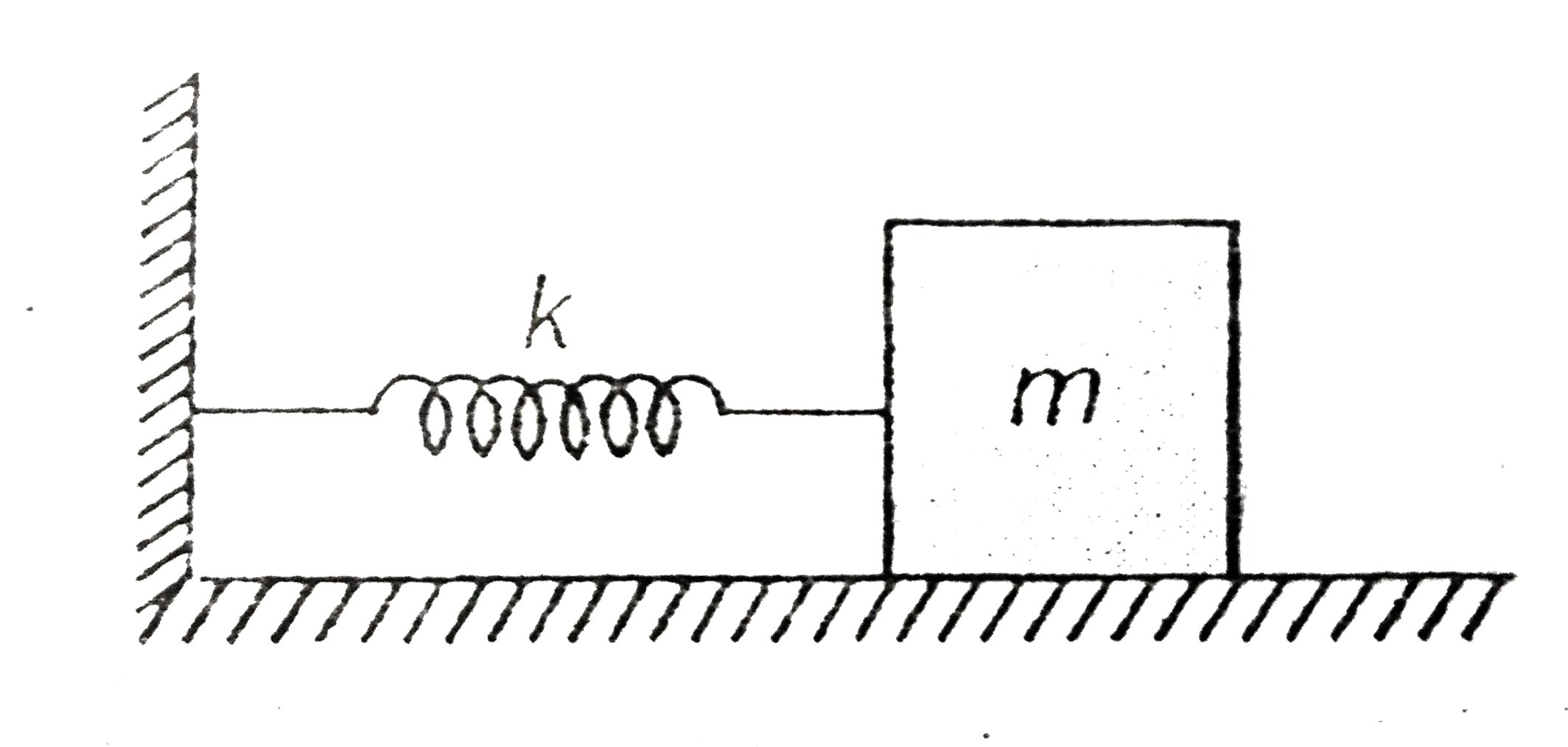
- Figure shows a block of mass 'm' resting on a smooth horizontal surfa...
Text Solution
|
- A : The work done by a force during round trip is always zero. R : Th...
Text Solution
|
- A : The change in kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the work do...
Text Solution
|
- A : Internal forces can change the kinetic energy but not the momentum...
Text Solution
|
- A : The potential energy can be defined only in conservative field. ...
Text Solution
|
- A : When a body moves in a circle the work done by the centripetal for...
Text Solution
|
- A : If net force acting-on a system is zero, then work done on the sys...
Text Solution
|
- A : During collision between two objects, the momentum of colliding ob...
Text Solution
|
- A : The potential energy of a system increases when work is done by co...
Text Solution
|
- A : In inelastic collision, a part of kinetic energy. convert into hea...
Text Solution
|
- A : Energy dissipated against friction depends on the path followed. ...
Text Solution
|
- A : Work done by the frictional force can’t be positive. R : Fricti...
Text Solution
|
- A : Impulse generated on one body by another body in a perfectly elas...
Text Solution
|
- A : Power of the gravitational force on the body in a projectile motio...
Text Solution
|
- A : Power delivered by the tension in the wire to a body in vertical c...
Text Solution
|
- A : When a man is walking on a rough road, that work done by frictiona...
Text Solution
|