A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS-PRACTICE SET 05-Paper 2 (Mathematics)
- If the eccentricity of a hyperbola is sqrt(3), the eccentricity of its...
Text Solution
|
- Equation of unit circle concentric with circle x^(2)+y^(2)+8x+4y-8=0...
Text Solution
|
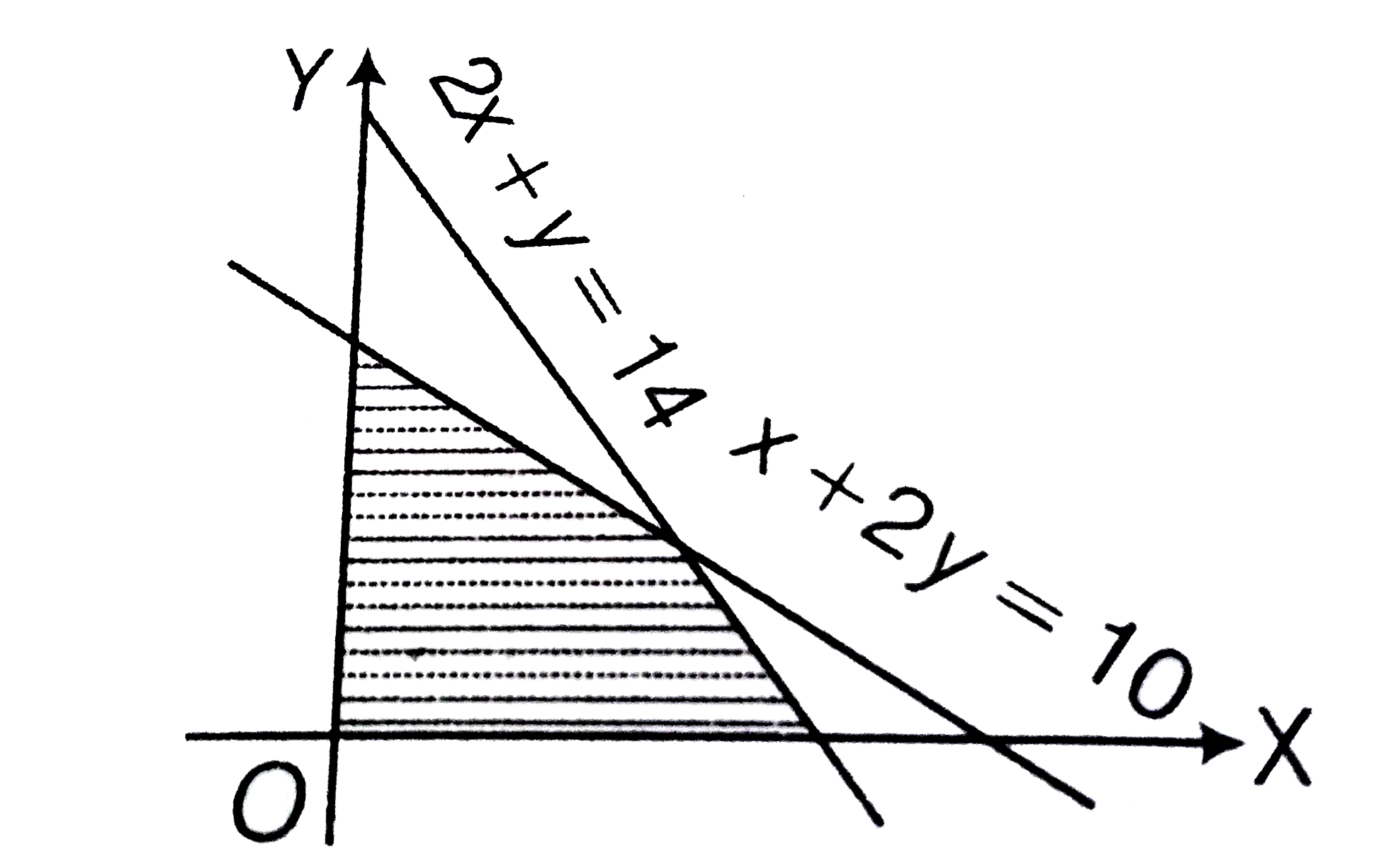
- The maximum value of objective function z=2x+3y in the given feasible ...
Text Solution
|
- The shown gate has an output is equal to
Text Solution
|
- The element in the first row and third column of the inverse of the ma...
Text Solution
|
- If p=DeltaABC is equilateral and q=each angle is 60^(@) then symbolic ...
Text Solution
|
- The area bounded by the curve y=x, X-axis and cordinates x=-1 to x=2, ...
Text Solution
|
- The feasible region of an LPP belongs to
Text Solution
|
- If sec((x^2-y^2)/(x^2+y^2))=e^a, then (dy)/(dx) is
Text Solution
|
- Give vectors x=3hati-6hatj-hatk, y=hati+4hatj-3hatk and x=3hati-4hatj-...
Text Solution
|
- The function f(x)=2x^3-15 x^2+36 x+4 is maximum at x= (a) 3 (b) 0 (c)...
Text Solution
|
- lim(x to 0) ((4^(x)-9^(x))/((4^(x)+9^(x)))) is equal to
Text Solution
|
- If y=sec^(-1)((x+1)/(x-1))+sin^(-1)((x-1)/(x+1)),x > 0. Find (dy)/(dx)...
Text Solution
|
- lim(x to 0) ((1+logx-x)/(1-2x+x^(2)) is equal to
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)={{:(0,x lt 0),(x^(2),xge0):}, then for all values of x
Text Solution
|
- For a random variable X, E(X)=3 and E(X^2)=11 Then, variance of X is
Text Solution
|
- int0^pix/(a^2cos^2x+b^2sin^2x)dx
Text Solution
|
- If (d^(2)y)/(dx^(2))+sinx=0, then the solution of differential equatio...
Text Solution
|
- int(a^(x//2))/(sqrt(a^(-x)-a^(x)))dx is equal to
Text Solution
|
- if x=loge t , t > 0 and y+1=t^2 then (d^2y)/(dx^2)
Text Solution
|