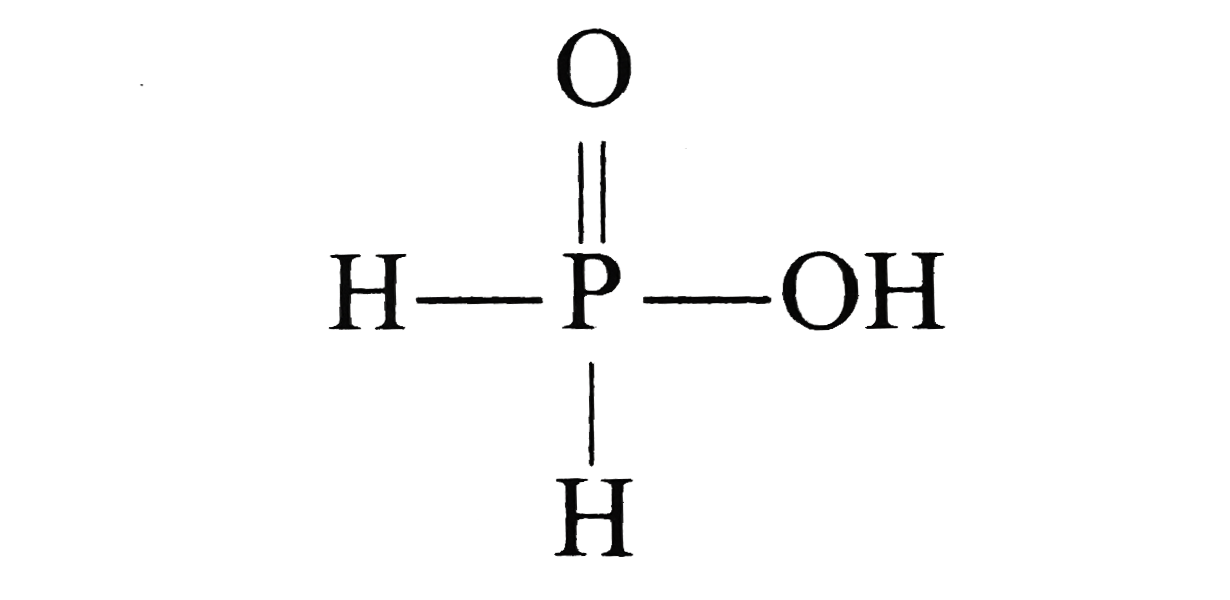Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Integer|16 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Multiple Correct|1 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Single Correct|85 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Ture False)|25 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives (Subjective)|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-STOICHIOMETRY-Exercises Assertion Reasoning
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): Hardness of water is determined by titrating it with di...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): Temporary hardness in water is due to the presence of c...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|
- (a). IF both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanatio...
Text Solution
|