A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|2 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Linked Comprehension|52 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|21 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|5 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2-Single Correct
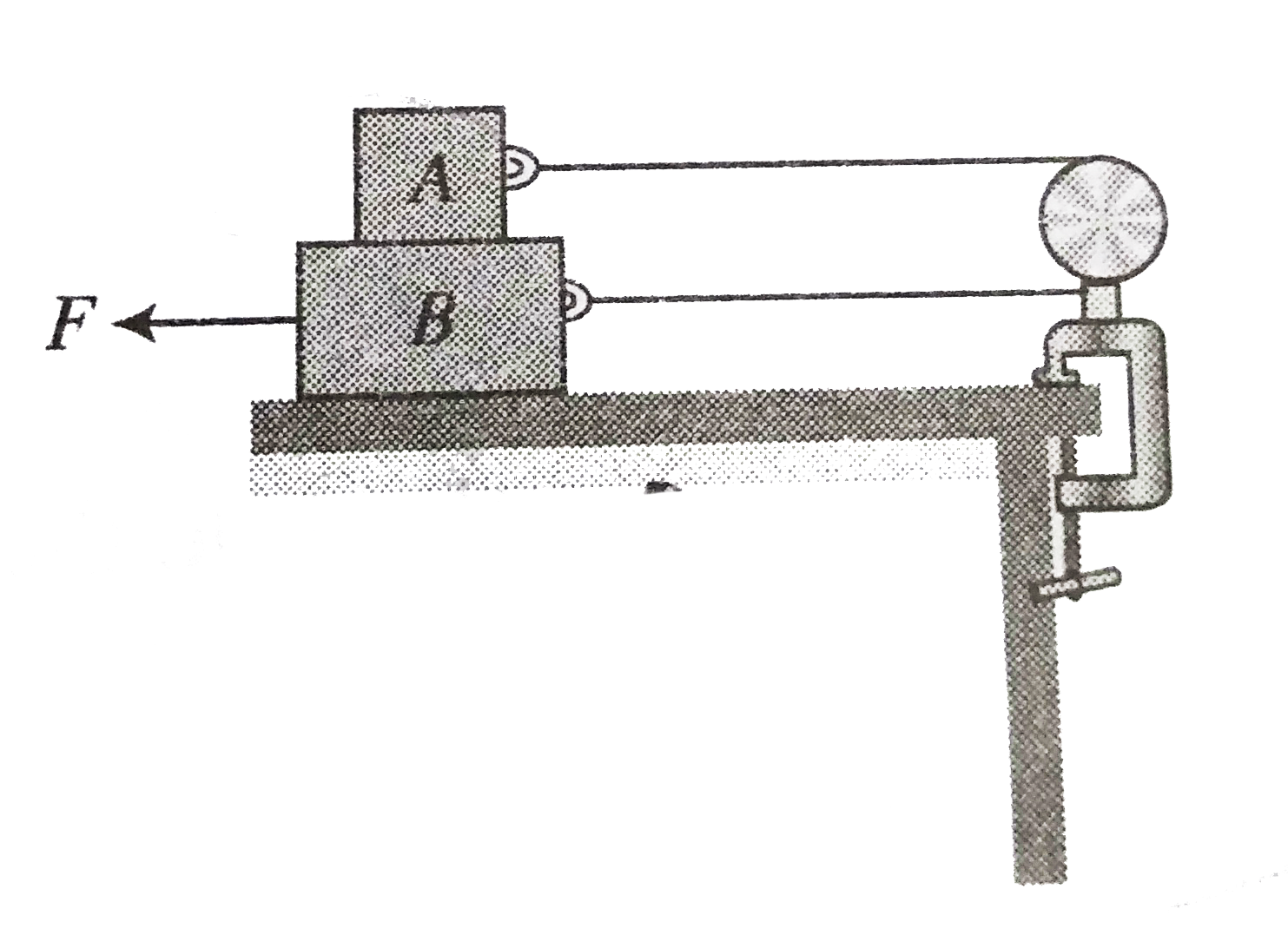
- If is problem - 57 all situation are same expect force is applied on b...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is being pulley along horizontal surface .The coeffi...
Text Solution
|
- Block A as shown in Fig weighs 2.0 N and block B weighs 6.0 N The coef...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a wooden block at rest in equilibrium on a rought horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2 kg is pushed against a rough vertical wall with a fo...
Text Solution
|
- A main revolves a stone of mass m tied to the end of a string in a cir...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius r is rotating about a vertical axis along its diamete...
Text Solution
|
- When the string of a conical pendulum makes an angle of 45^(@) with th...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical particles are joined together by a thread as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical particles are attached at the end of a light string whic...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is revolving in a smooth horizontal plane with a con...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with a speed v(0) = sqrt(gR). The coefficient ...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels with constant speed on a circular road level ground in f...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is projected on a smooth horizontal circular track w...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B start racing at the same on a flat race track which c...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the setup is of a Ferris wheel in an amusement part. The whee...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected through a massless in...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig if F = 4N , m= 2 kg M = 4 kg then
Text Solution
|
- A 20 kg blocks is placed on of 50 kg block as shown in figure An horiz...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of masses m(A) and m(B) have velocity v and 2v res...
Text Solution
|