Difference in level of liquids, `h_(1)=20 cm=0.2 m`
Pressure of the gas in the containing, `p_(1)=p_(a)+rhogh_(1)`
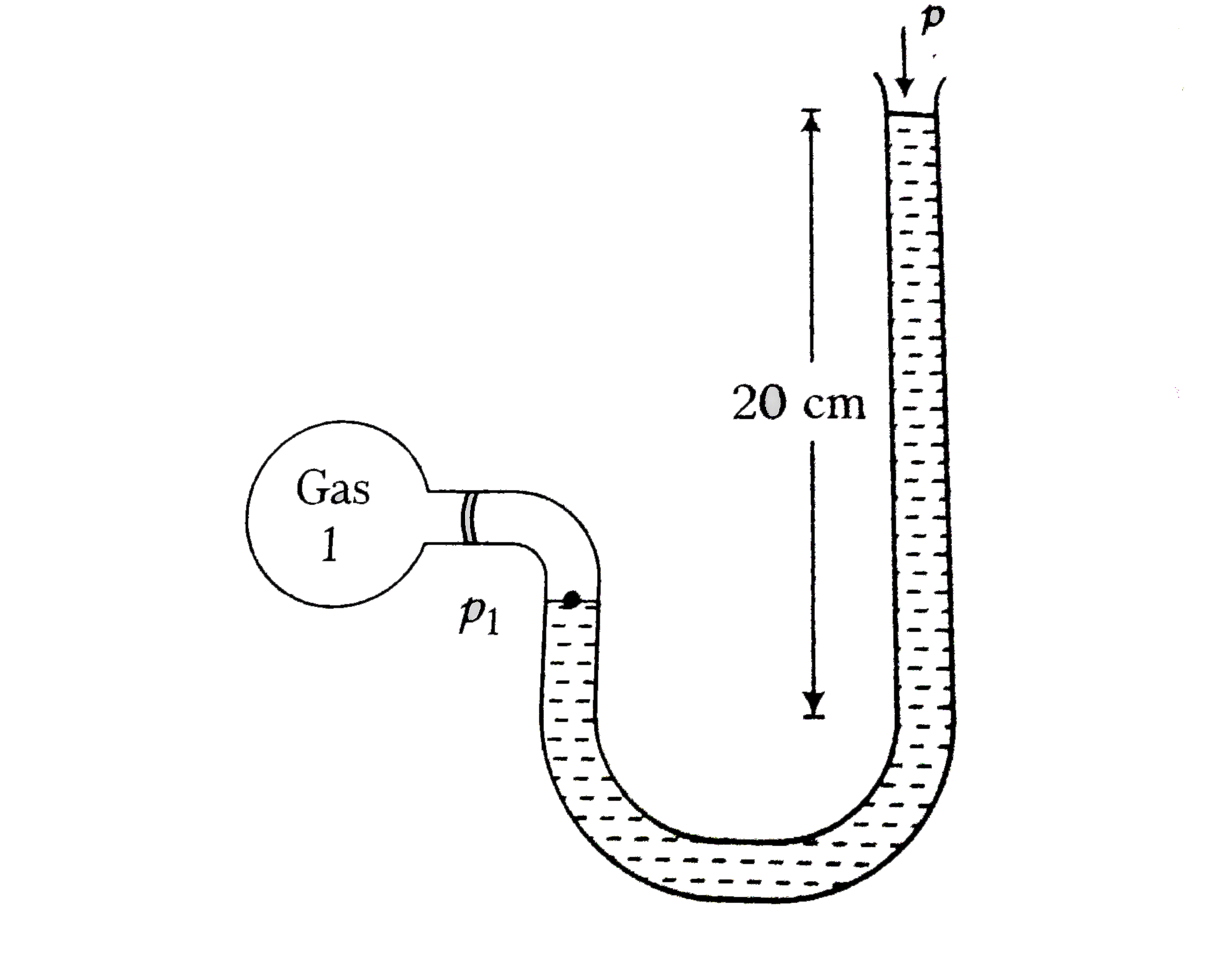
In this case, level of the liquid in the left arm is higher than that in the right arm by 8 cm.
`therefore` Atmospheric pressure `p_(a)` is greater than the pressure exerted by the sample
`implies p_(a)=p_(2)+rho gh_(2) implies p_(2)=p_(a)-rho gh_(2)`
Comparing equations (i) and (ii), it is clear that `p_(1) gt p_(2)`.
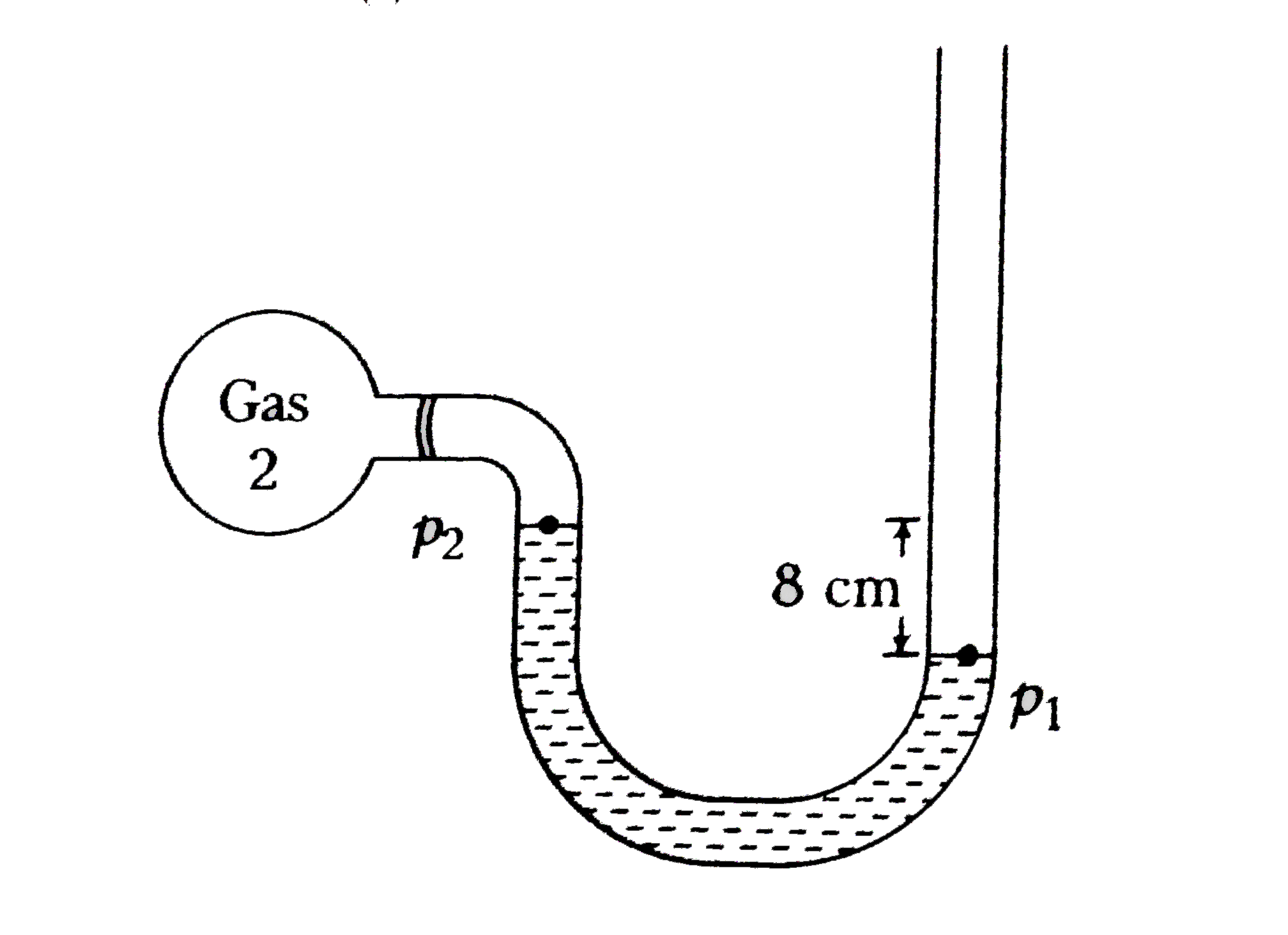
Therefore the gas in sample 1 exerts greater pressure than that in sample 2.
The difference in the two pressures is
`p_(1)-p_(2)=(p_(a)+rhogh)(1)-(p_(a)-rhogh_(2))`
`=rhog(h_(1)+h_(2))`
`=rhog(28 cm)`
`=(3xx10^(3) kg m^(-3))xx(9.8 ms^(-2))(0.28 m)`
`=8.23xx10^(3) Pa ~~8 k Pa`