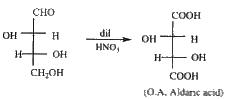A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-4|30 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-5|30 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-2|30 VideosBIOMOLECULES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCISE-4 (ASSERTION (A) & REASON (R) TYPE QUESTIONS :)|84 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (Integer Type Questions)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-CARBOHYDRATES-Practice Sheet-3
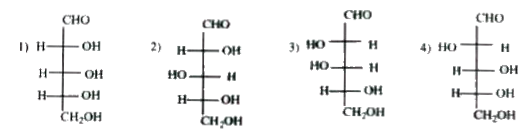
- Which of the following is the correct Fischer representation of D-gala...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement about the pyranose form of mannose is...
Text Solution
|
- Two aldopentoses X and Y give the same osazone derivative. X is oxidiz...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct set of stereochemical relationship among the foll...
Text Solution
|
- D-glucose overset(HO^(-))hArr A+ B A and B are
Text Solution
|
- Which of the molecules below will react with alcohol?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the compounds (A-C) depicted above is NOT a hemiacetal linkag...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following represents the anomer of the compound shown?
Text Solution
|
- Which set of terms correctly identifies the carbohydrate shown ? ...
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement about the following disaceharide is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are true regarding mutarotaion?
Text Solution
|
- What is/are true regarding epimers and epimerization?
Text Solution
|
- What is /are true regarding (+) maltose-a disaccharide?
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement is/are
Text Solution
|
- What is /are true regarding amylose?
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers C(4)H(4)O(4) of dicarboxylic acid both decolorise ...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers C(4)H(4)O(4) of dicarboxylic acid both decolorise ...
Text Solution
|
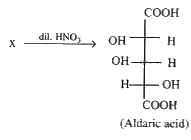 This has no plane of symmetry and hence optically active
This has no plane of symmetry and hence optically active