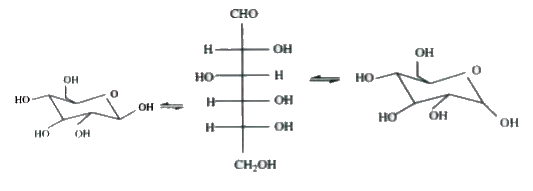
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-4|30 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-5|30 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-2|30 VideosBIOMOLECULES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCISE-4 (ASSERTION (A) & REASON (R) TYPE QUESTIONS :)|84 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (Integer Type Questions)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-CARBOHYDRATES-Practice Sheet-3
- The correct statement about the following disaceharide is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are true regarding mutarotaion?
Text Solution
|
- What is/are true regarding epimers and epimerization?
Text Solution
|
- What is /are true regarding (+) maltose-a disaccharide?
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement is/are
Text Solution
|
- What is /are true regarding amylose?
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 140^(@)C and specific rotation [a](D)^(...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers C(4)H(4)O(4) of dicarboxylic acid both decolorise ...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers C(4)H(4)O(4) of dicarboxylic acid both decolorise ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Number of ATP molecules involved in the synthesis of each molecule of ...
Text Solution
|
- How many of them are non reducing sugars among the following: Glucose,...
Text Solution
|
- When glucose is reacted with bromine water the major product is 'x', i...
Text Solution
|
- In lactose Number of mono saccharide units are present
Text Solution
|
- Number of Functional groups are present is saccharides (comonly)
Text Solution
|
- In the formation of Raffinose how many water molecules are eliminated ...
Text Solution
|