Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|87 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|2 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 7.3|27 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|5 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2-Subjective
- Block A as shown in figure weight 1.40 N and block B weight 4.20 N The...
Text Solution
|
- Two block , with masses m(1) and m(2) are staked as shown in fig and p...
Text Solution
|
- Block A has a mass of 30 kg and block B a mass of 15 kg . The coeffici...
Text Solution
|
- Block A weight 20 kg placed on a smooth surface. Weight B of 2 kg is m...
Text Solution
|
- In figure find the acceleration of m assuming that there is friction b...
Text Solution
|
- The masses of the block A and B are m and M Between A and B there is a...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m and M are connected by a chord passing around a ...
Text Solution
|
- A block with mass m(1) is placed on an inclined plane with slope angle...
Text Solution
|
- Consider three blocks placed one over the other as shown in Fig. Let a...
Text Solution
|
- Four block are arranged on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pressed against a wall which is moving with an ac...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure pulleys are mass of block A,b and C...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure mass of blocks A,B and C is 18.5 kg...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block is experiencing three forces F(1) = 20 N acts at angle...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m = 3 kg is resting over a rough horizontal surface ha...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of the wedge shown in fig is M = 4 kg and that of block is m...
Text Solution
|
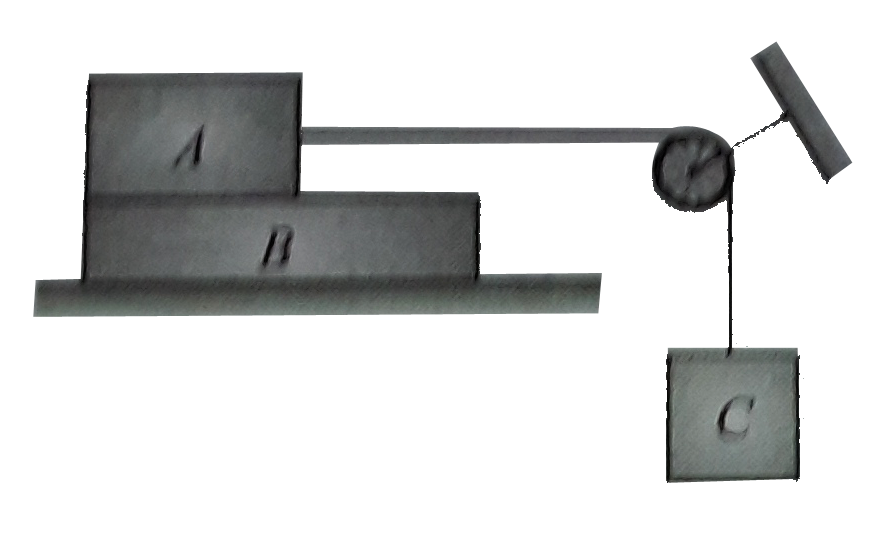
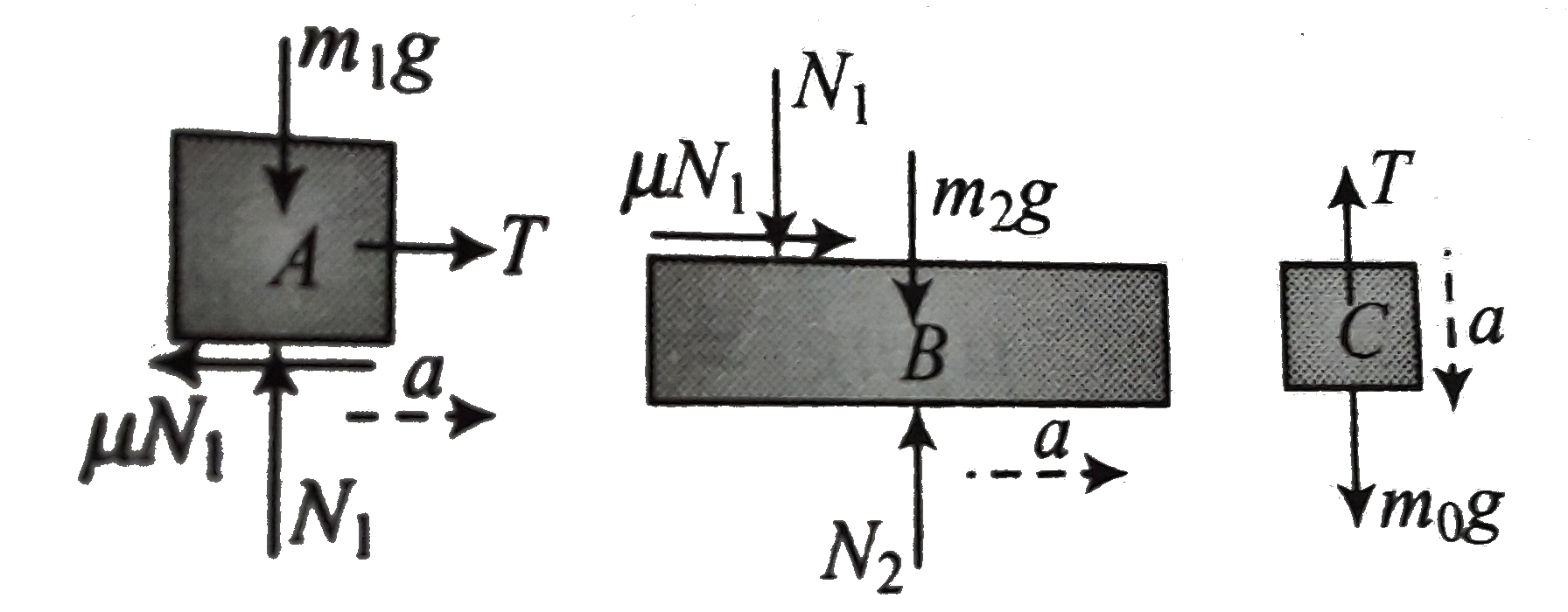
- Calculate the maximum possible value of mass m(0) of block C upto whic...
Text Solution
|
- With two hands you hold a cone motionless upside doen , as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A prismatic block of mass m is kept on a groove . The bottom line of t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m(1) connected with another of mass m(2) by a light s...
Text Solution
|